Usage¶
Note
You'll have to install the package first. See https://wasi-master.github.io/pypi-command-line/install for instructions.
Tips
- You can click the gifs to make them restart, if this does not work reload the page (Shortcut for reloading: F5)
- You can either
- right click and press "Open Image in New Tab" to open them in full screen
- drag the image and drop it to your tabs panel to open them in full screen
Options¶
-h, --help¶
Sends a help message, each command also has this flag that you can use to see the help about that specific command
Usage¶
pypi -h
pypi --help
For command specific help: (search in this case)
pypi search --help
--install-completion¶
Installs autocompletion for the current shell.
Demo¶

Usage¶
pypi --install-completion
--show-completion¶
See code for autocompletion for the current shell, to copy it or customize the installation.
Demo¶
The output will be different depending on the shell
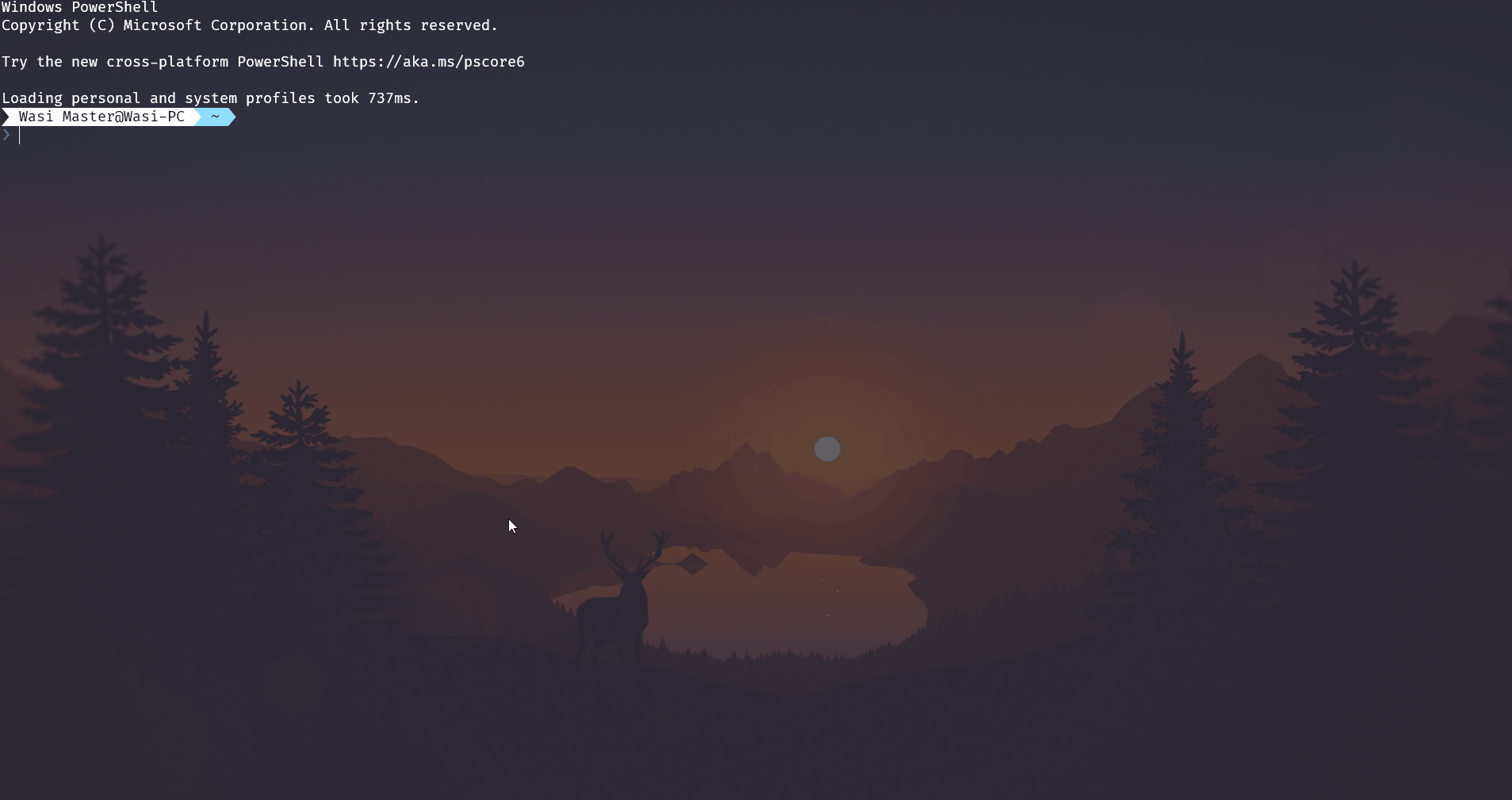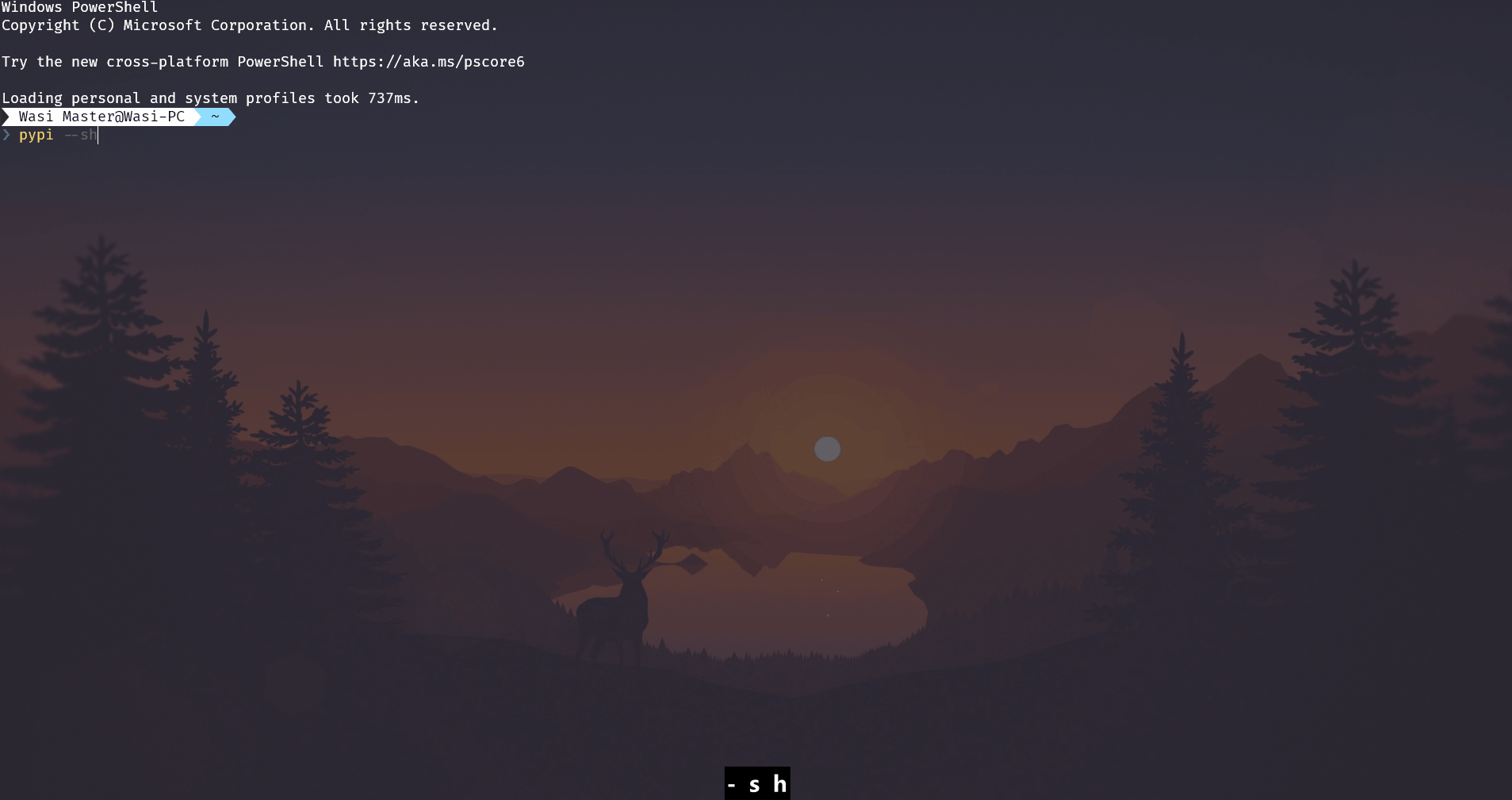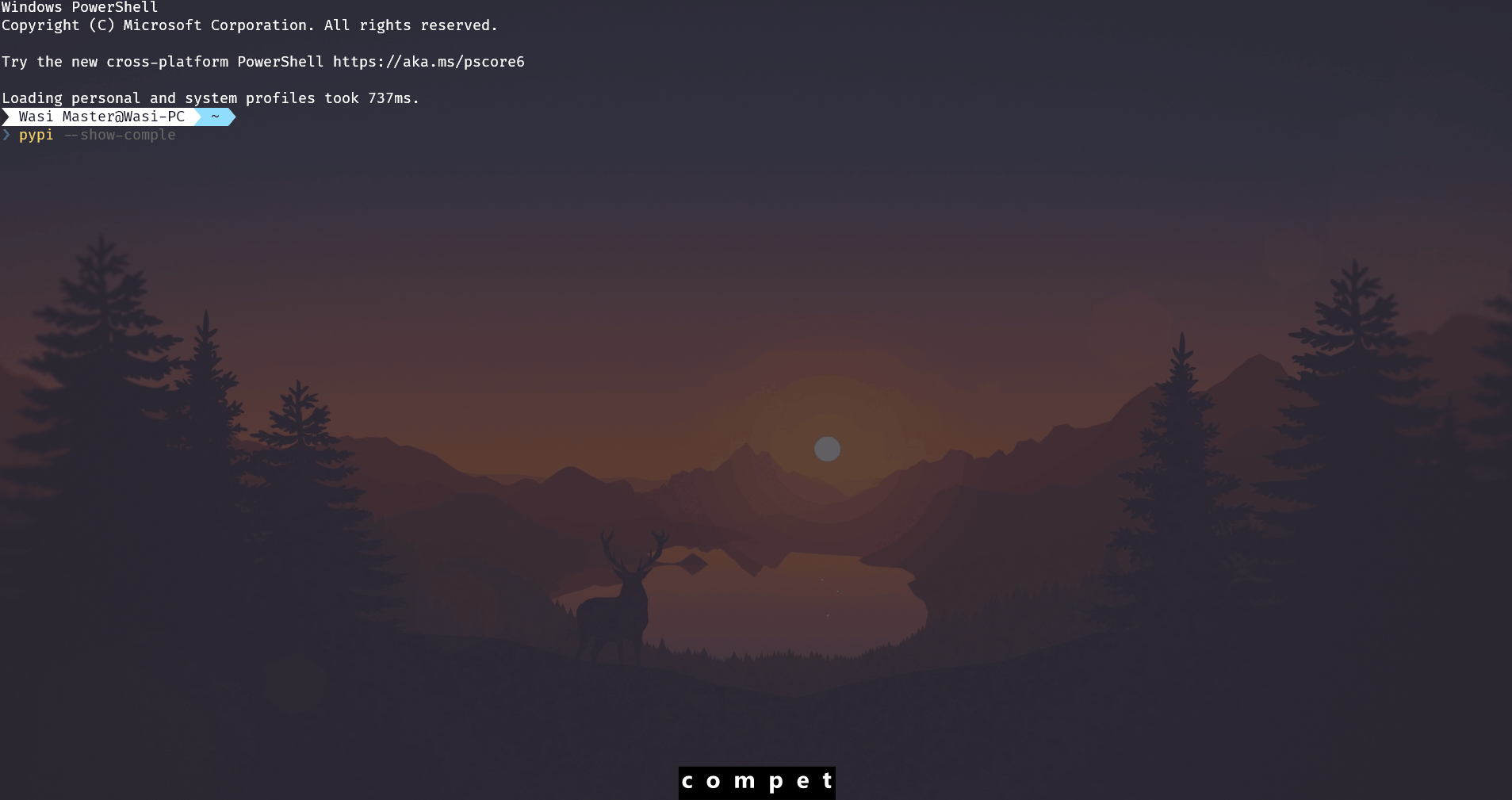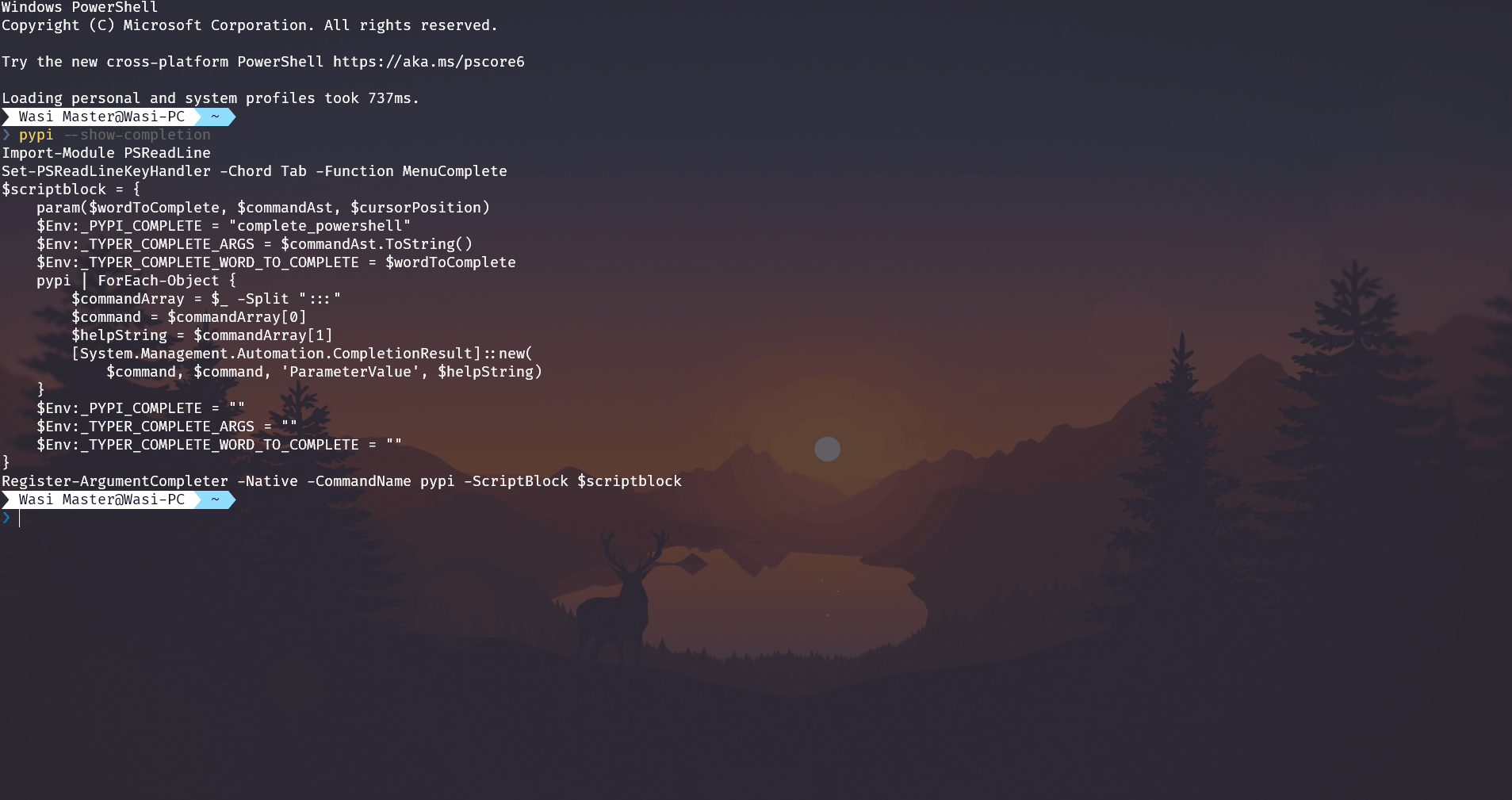
Usage¶
pypi --show-completion
--no-cache¶
If used, disabled the cache for the current command, for more information about the cache see notes
Demo¶
TODO: Add demo for --no-cache
Usage¶
pypi --no-cache
--repository¶
Specify a base url for the repository from which the results are taken from. Such as testpypi
Demo¶
TODO: Add demo for --repository
Usage¶
pypi --repository testpypi
pypi --repository https://test.pypi.org
Commands¶
version¶
See the latest version of any package or pypi-command-line if no package was specified
How this works is if you specify a package name then it shows the top limit latest versions of that specified package, otherwise it shows the current version of pypi-command-line and the latest version of pypi-command-line
Demo¶
Seeing the current and latest version of pypi-command-line:

Seeing the latest versions of another package (django in this case):
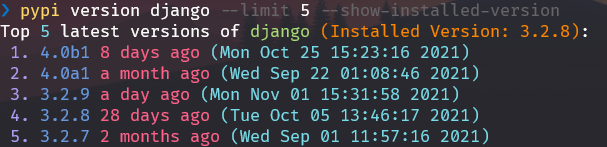
Omitting the pre-releases:

Usage¶
pypi version [PACKAGE_NAME]
Options¶
-
PACKAGE_NAMEThe name of the package to show the latest version(s) for. [default: pypi-command-line]
-
--limit INTEGERLimit the number of versions to show [default: 10]
-
--no-pre-releasesIf set then it will not show pre-releases
-
--show-installed-versionsIf set then it will show the version that is installed too
-
-h,--helpShow the help message.
browse¶
Browse for a package's URLs.
This gets the package information, and shows a list containing it's project urls. If the project has a maintainer email set then it also shows that as a mailto[?] that you can press to send a email via your default email client. This gets all the project urls from PyPI and then shows them, there is a known bug where PyPI in some cases shows UNKNOWN for some url so that also gets shown.
Demo¶
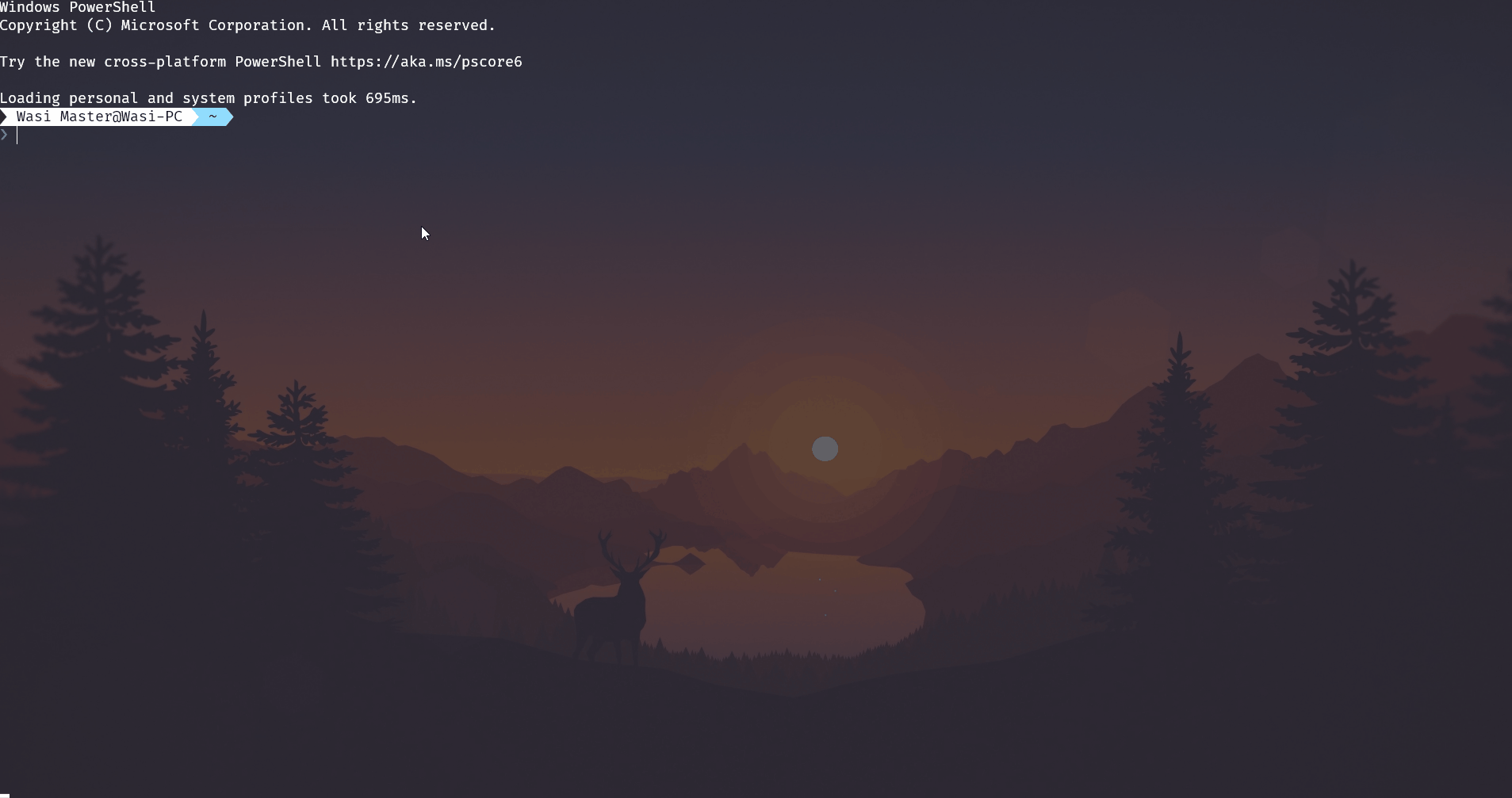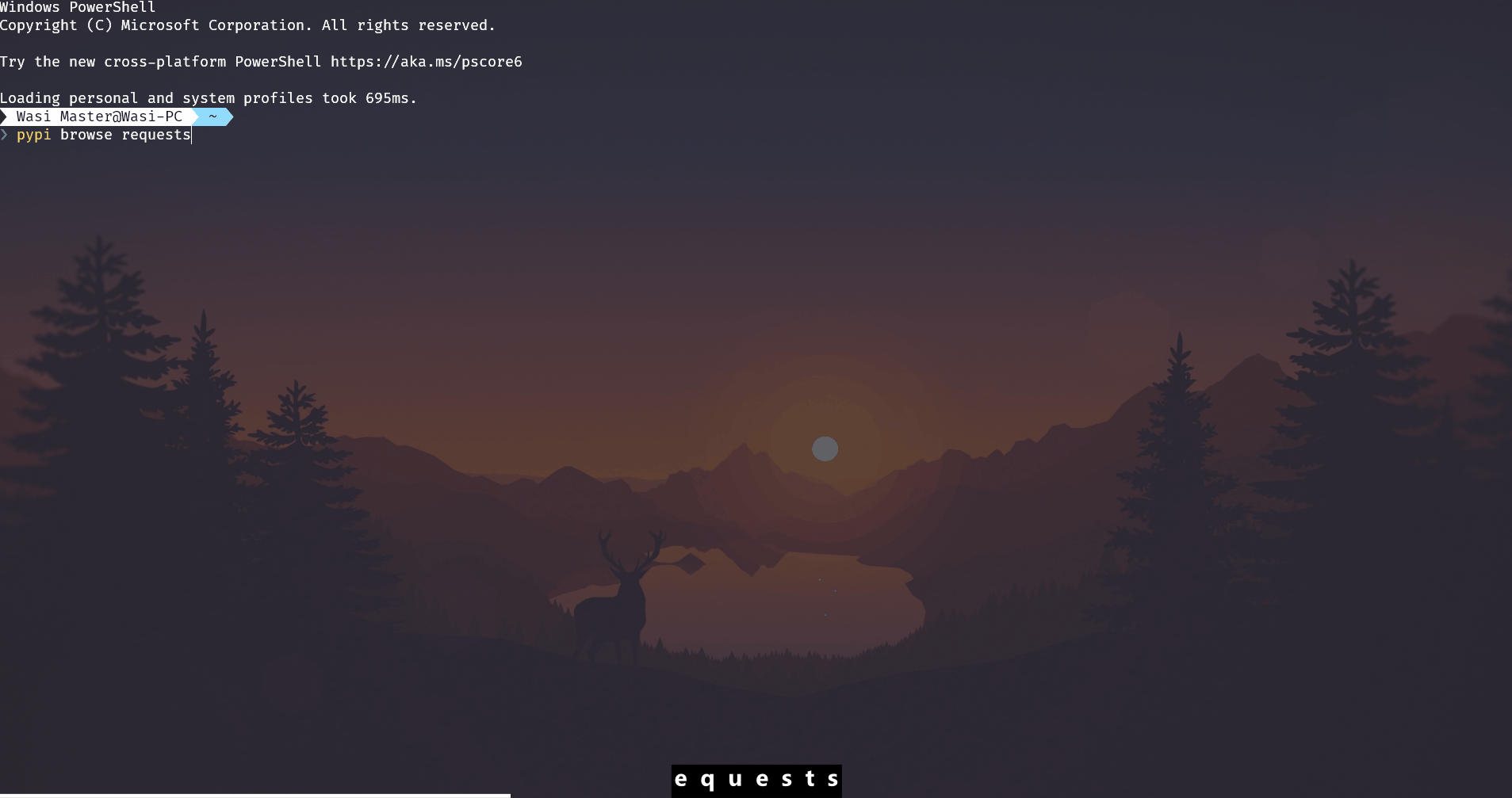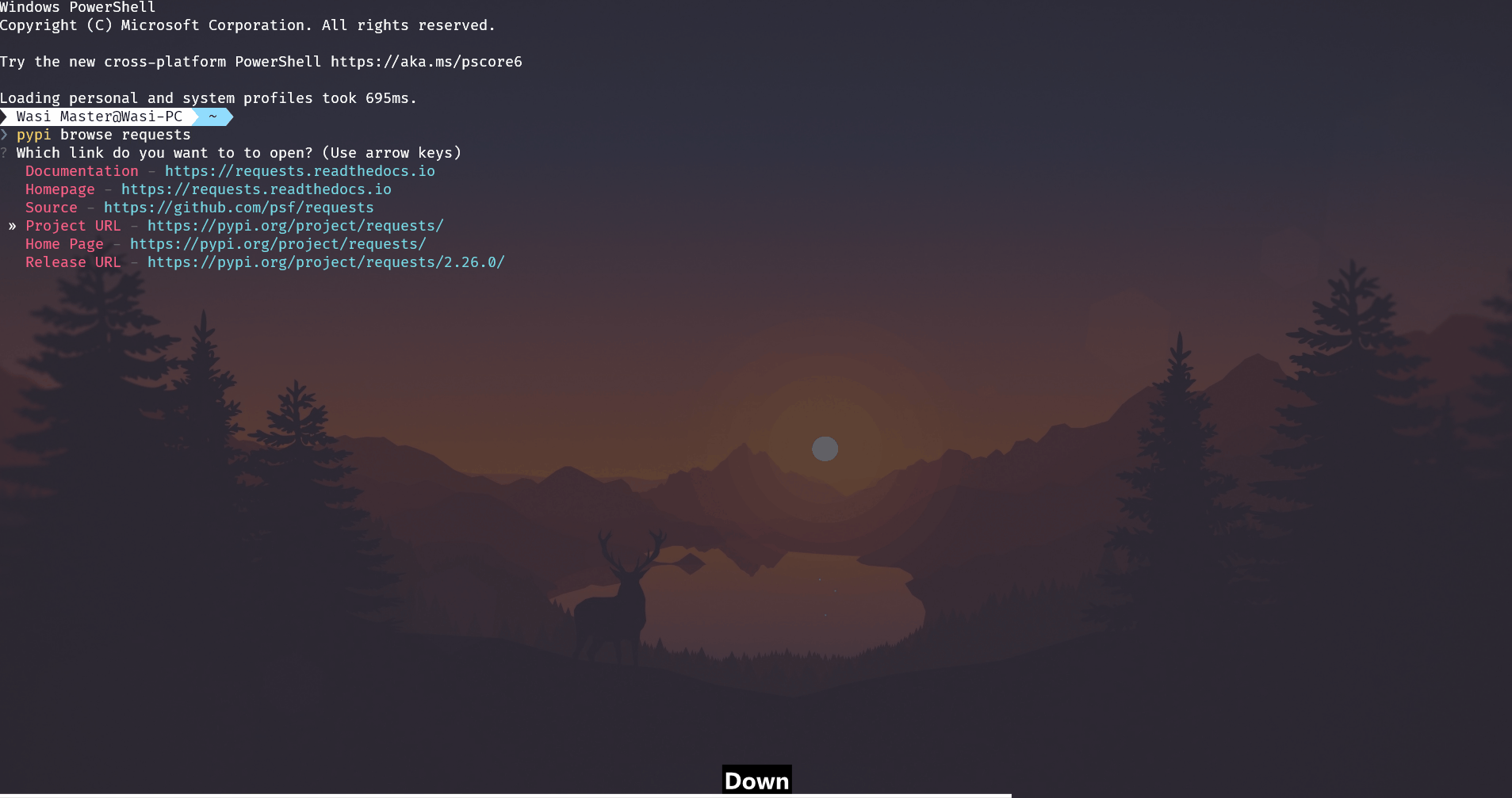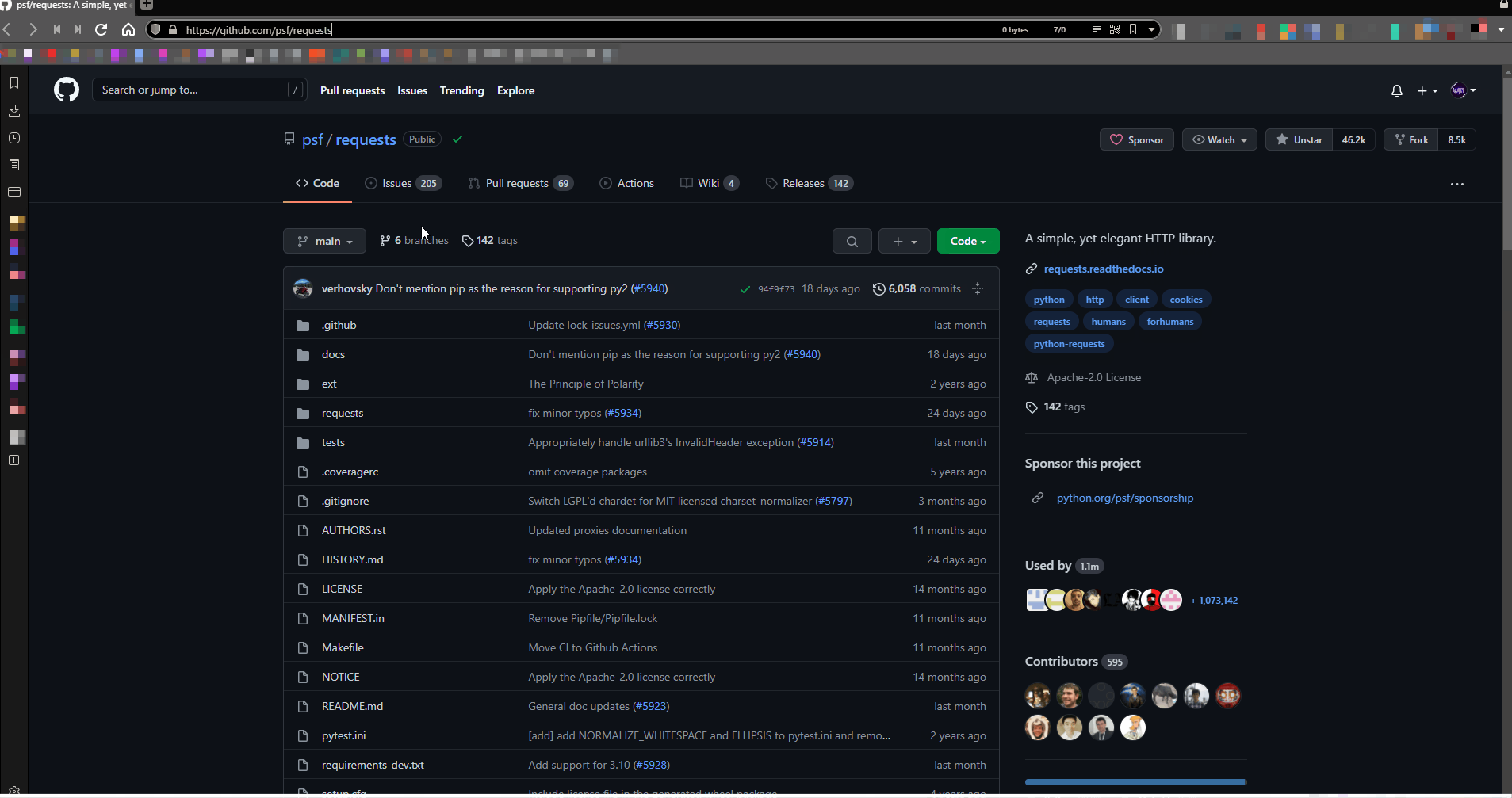
You can cancel using Ctrl+C if you don't find your desired link

Usage¶
pypi browse PACKAGE_NAME
Options¶
-
PACKAGE_NAMEThe name of the package to show the urls for. [required]
-
--url-onlyOnly show urls of the package instead of showing an interactive dialog to open in a web browser.
-
-h,--helpShow the help message.
cache-clear¶
Clears the local packages and requests cache, see notes for more information about the cache.
Usage¶
pypi cache-clear
Errors and Warnings¶
-
E: Failed to delete
<file_path>¶Shown when it cannot delete a file due to some other process using it or not having enough permissions
cache-information¶
Shows the size for the packages cache and the size and additionally the websites cached with their creation date and expiry date, see notes for more information about the cache.
Errors and Warnings¶
-
W: Packages cache not available¶
Shown when the packages cache doesn't exist due to it not being created yet or being deleted recently. You can rebuild that cache using
cache-refresh -
W: Requests cache not available¶
Shown when the requests cache doesn't exist due to the
requests-cachepackage not being installed
Usage¶
pypi cache-information
cache-refresh¶
Reloads the packages cache and shows the number of new packages added after the last refresh, see notes for more information about the cache.
Usage¶
pypi cache-refresh
description¶
Shows the description of a package as gotten from PyPI or GitHub.
This first gets the information about the package and then finds the descripton. If the package has a descripton it gets the description format, if it's reStructuredText or Markdown then it shows the description formatted according to the format.
If it doesn't get a description in PyPI then it looks for github repos mentioned in the json response gotten from the pypi api. this makes sure it gets the repo if it is supplied no matter where it is. If it finds multiple repos then it asks the user to pick one. Then it uses the github api to find the name of the readme file of the repo, this uses the api instead of manually finding it just in case. Then it reads the contents from the readme file and determines the format using the file extension then it shows the description formatted according to the format.
Demo¶
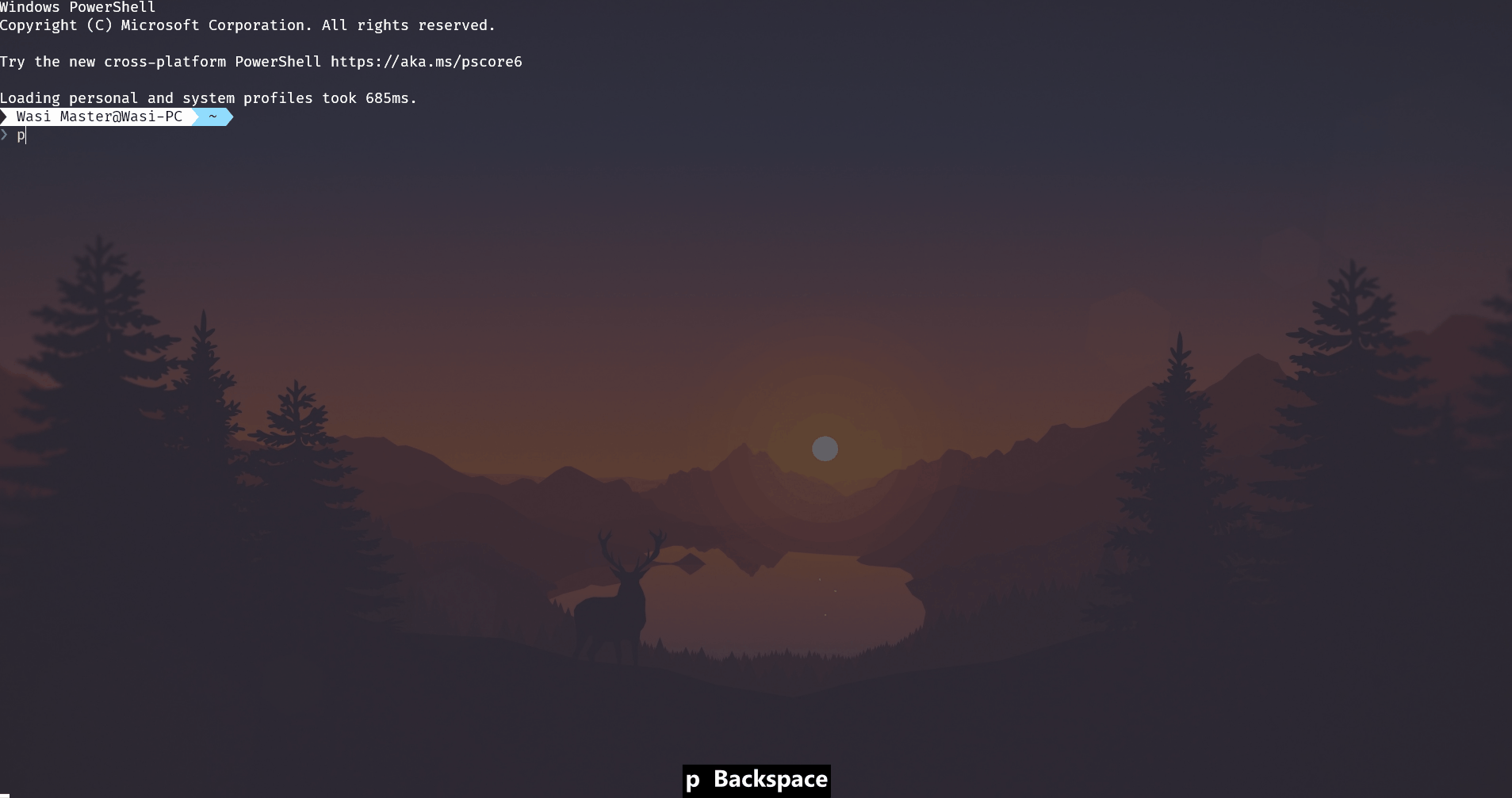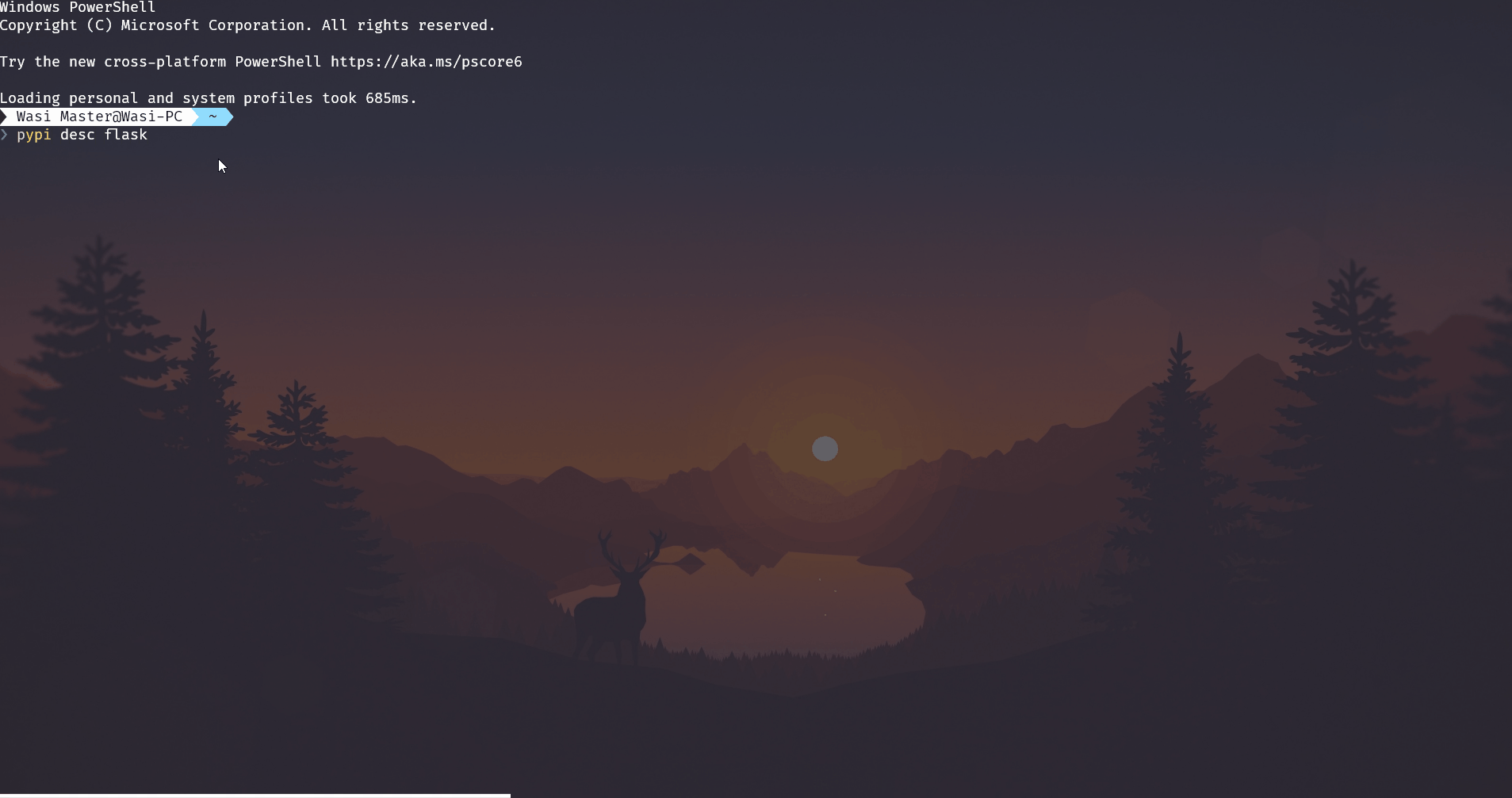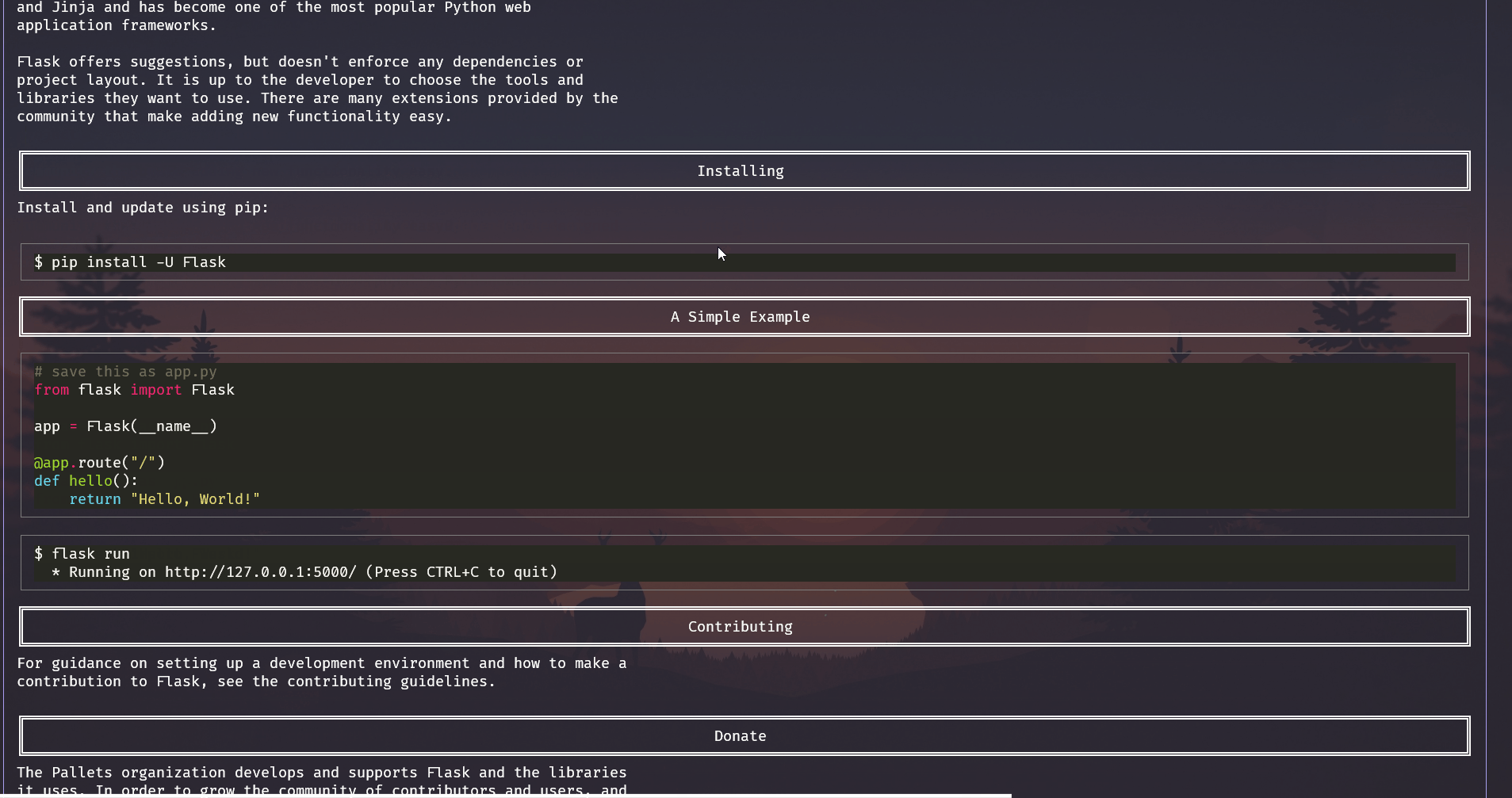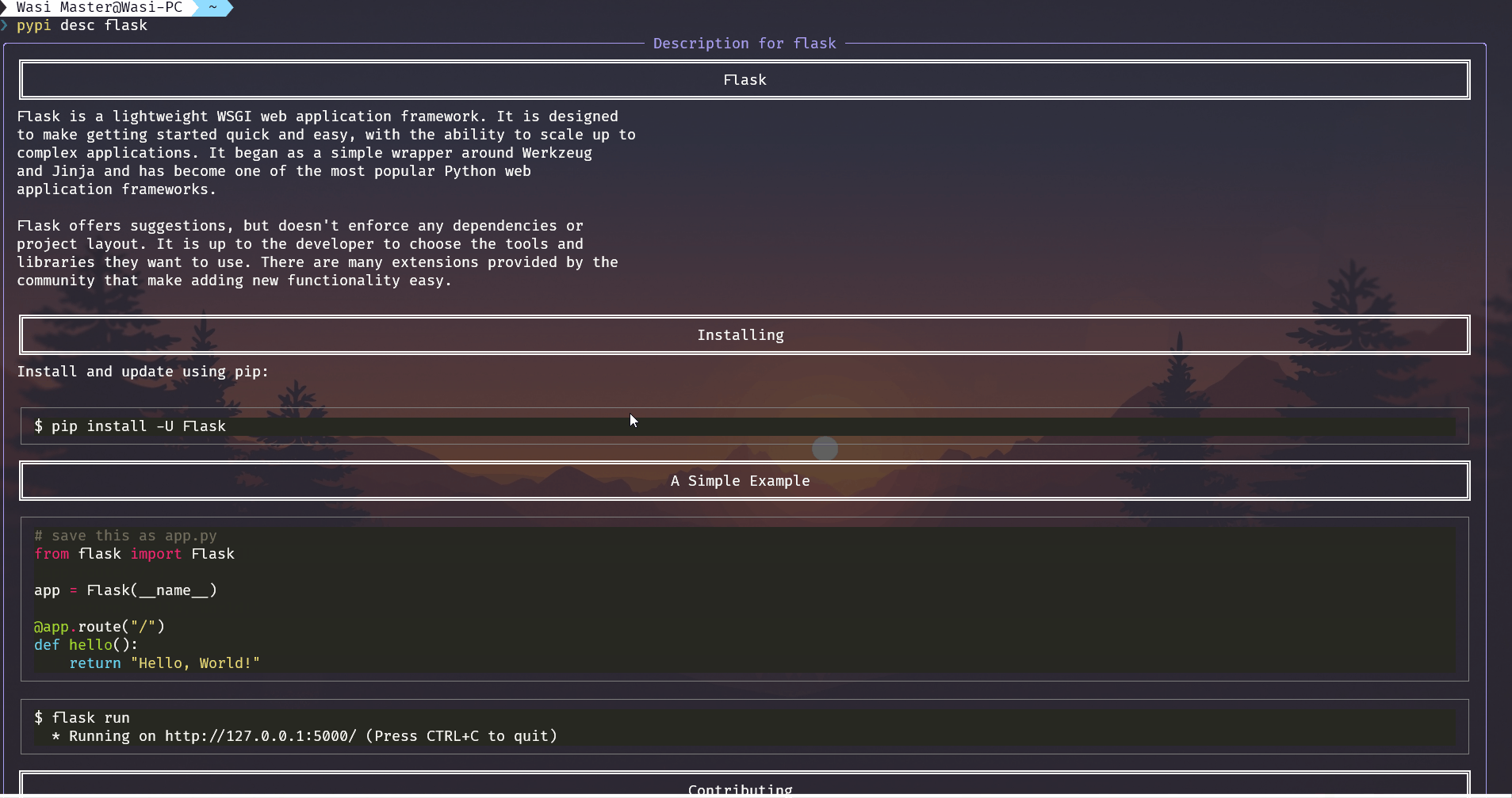
Demo of getting description from github if pypi does not have one

Usage¶
pypi description [OPTIONS] PACKAGE_NAME
Options¶
-
PACKAGE_NAMEPackage to get the description for [required]
-
--force-githubForcefully get the description from github This will make sure that it doesn't get the description from pypi but get it from github by reading the readme file of that project's repository
-
--syntax-themeSpecify a custom syntax highlighting theme for code blocks This has to be a pygments supported syntax highlighting theme or
ansi_darkoransi_lightwhich will use the colors from your terminal theme. For a list of pygments themes see this link -
-h,--helpShow the help message.
Errors and Warnings¶
-
E: Project not found¶
Shown when the pypi api returns a 404 response meaning a package with the specified name most likely doesn't exist
-
E: ReadMe not found¶
Shown when
--force-githubis enabled or the PyPI page doesn't have a description and the github page also doesn't have a readme -
W: Multiple github repos¶
Shown when
--force-githubis enabled or the PyPI page doesn't have a description. If this is shown it will ask you to pick one
information¶
The information command gets data from PyPI and GitHub and PyPIStats and shows them to the console
Demo¶
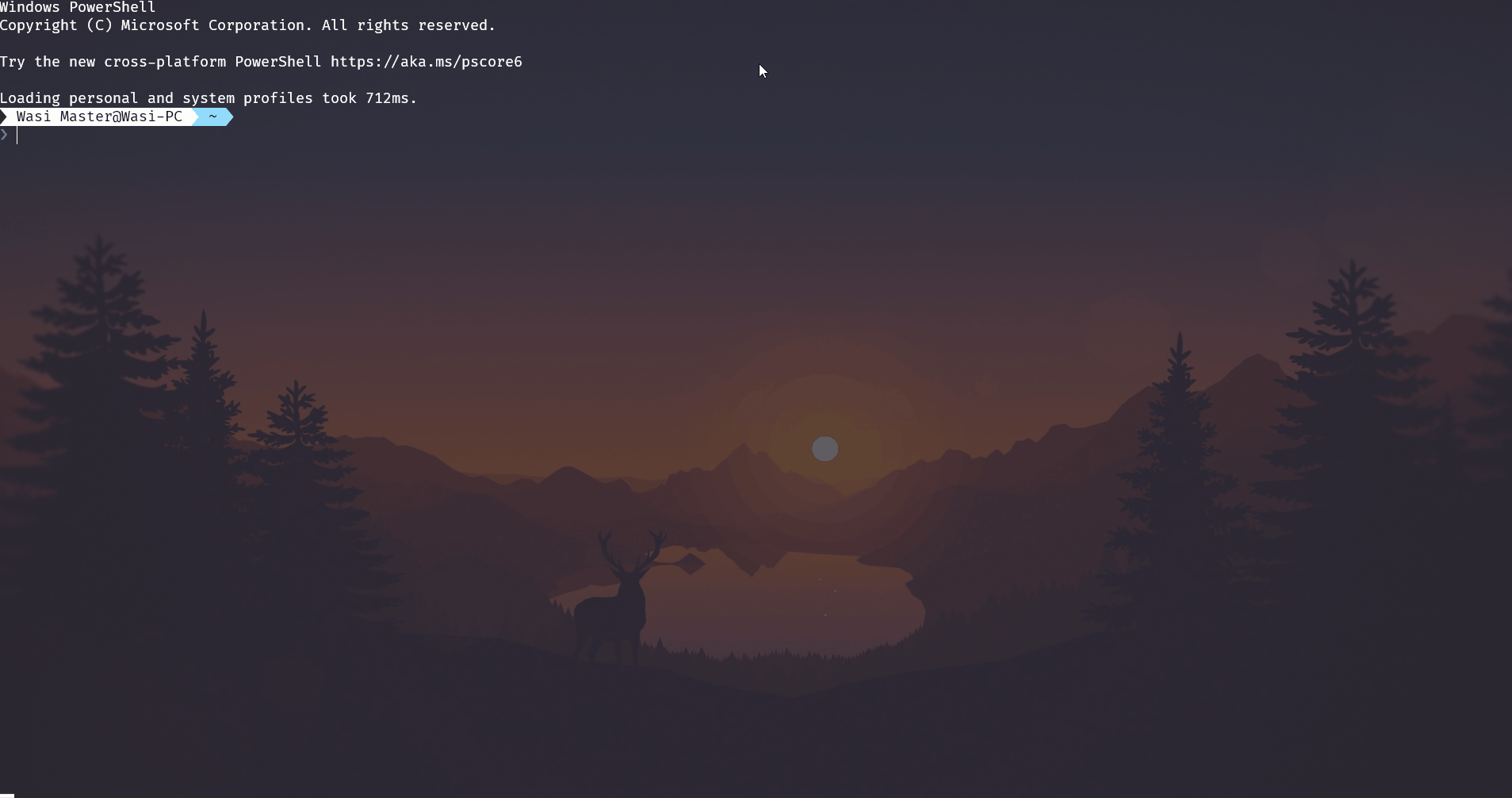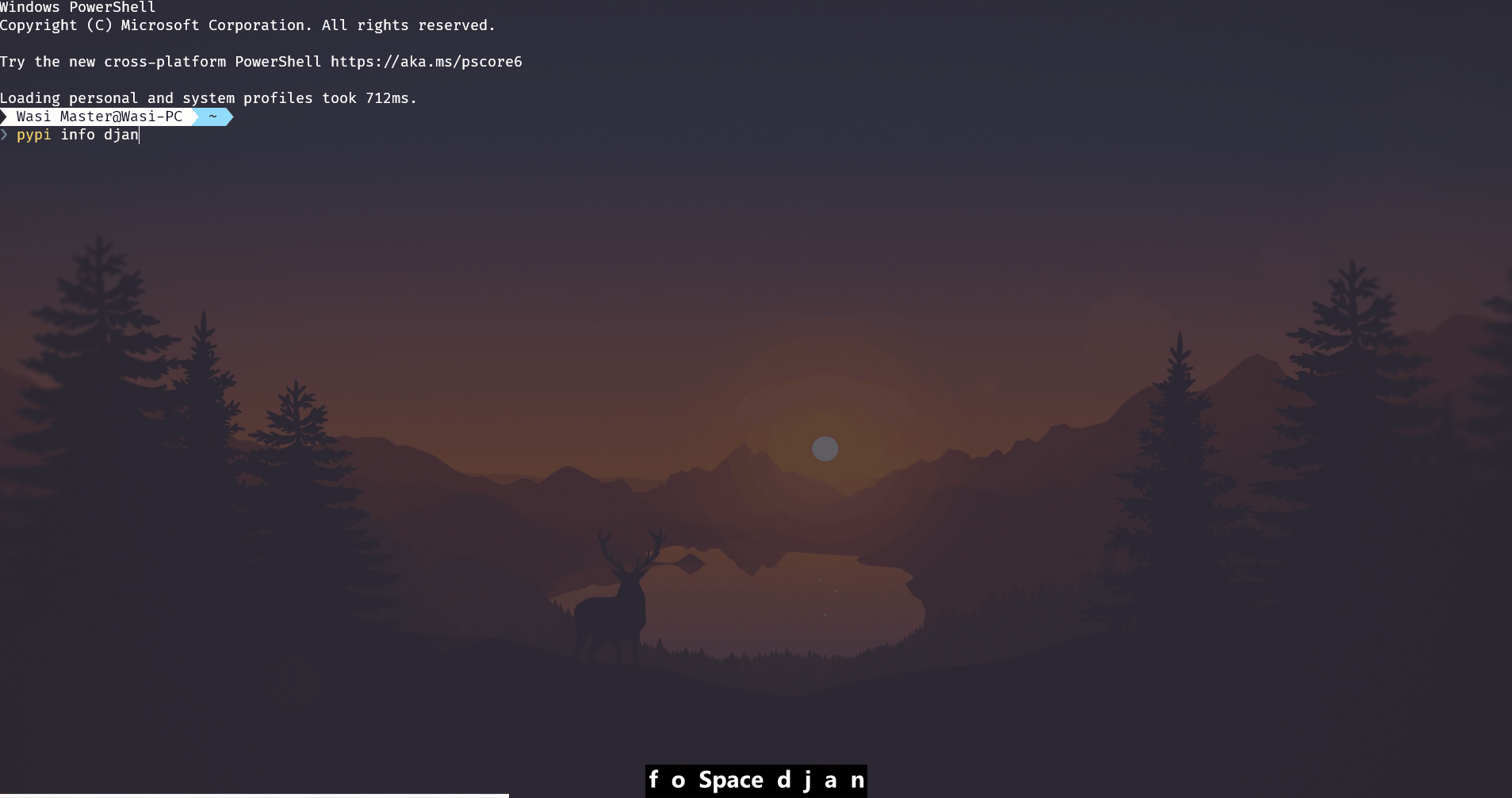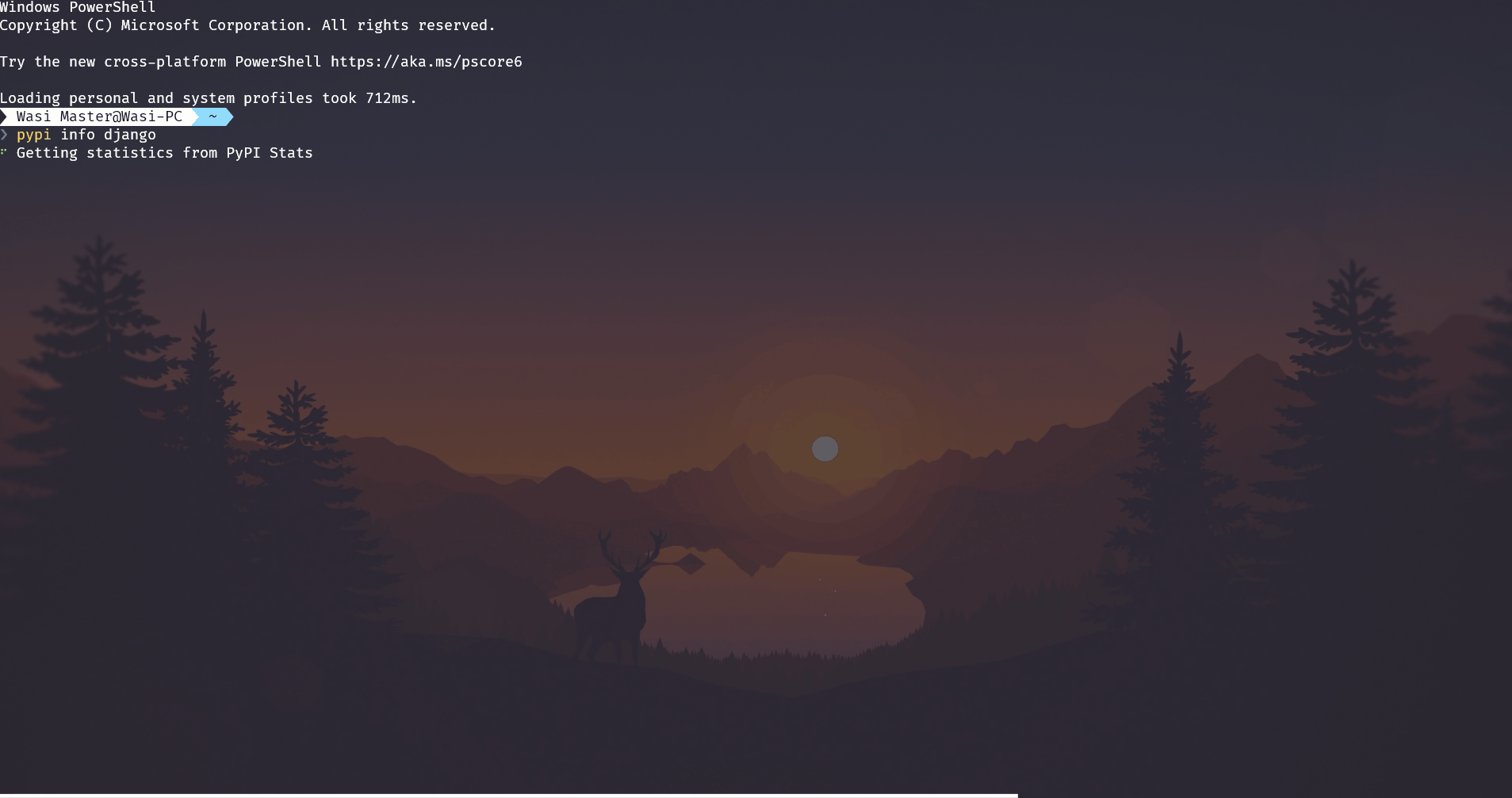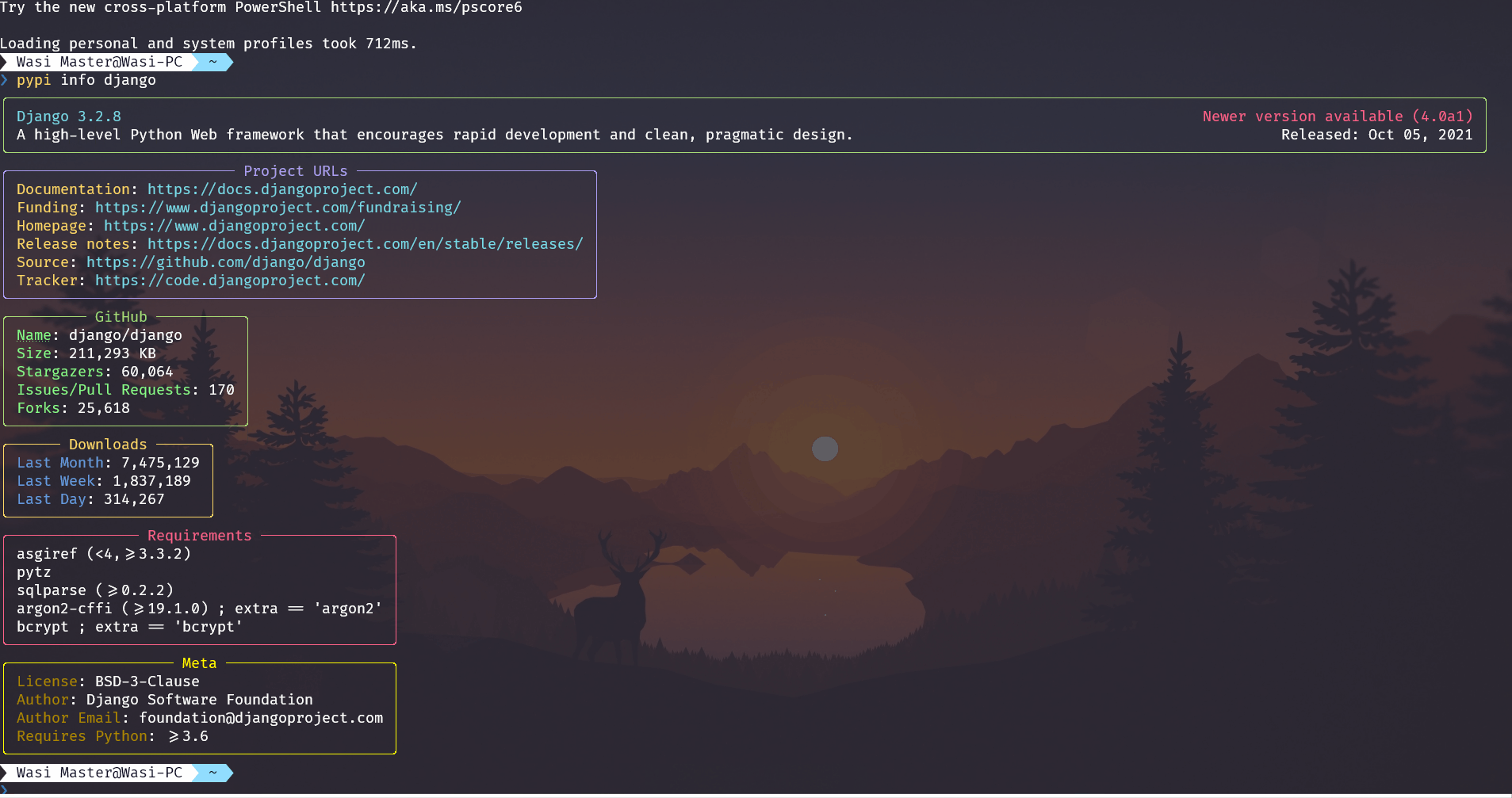
You can also see classifiers if you want to
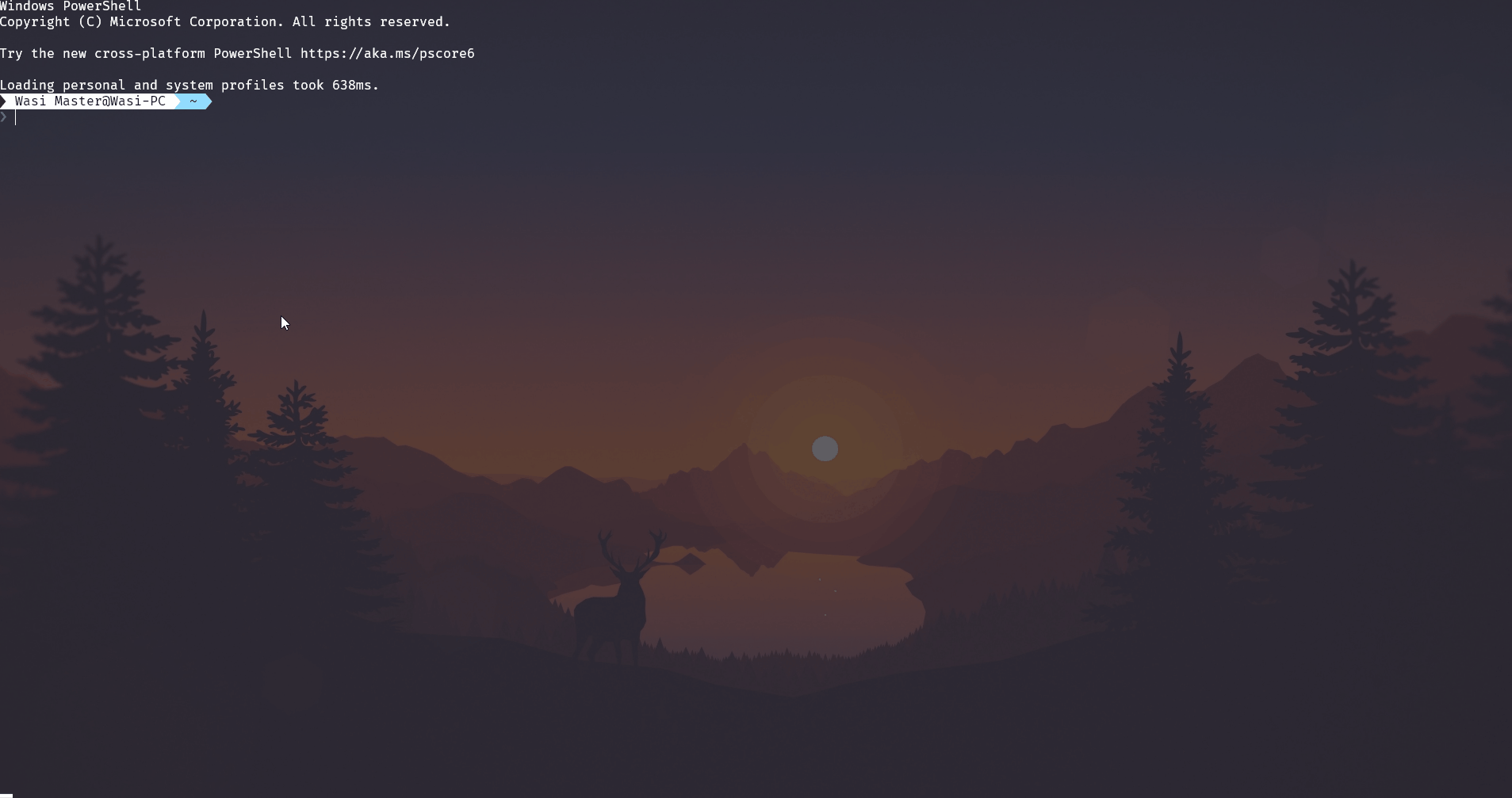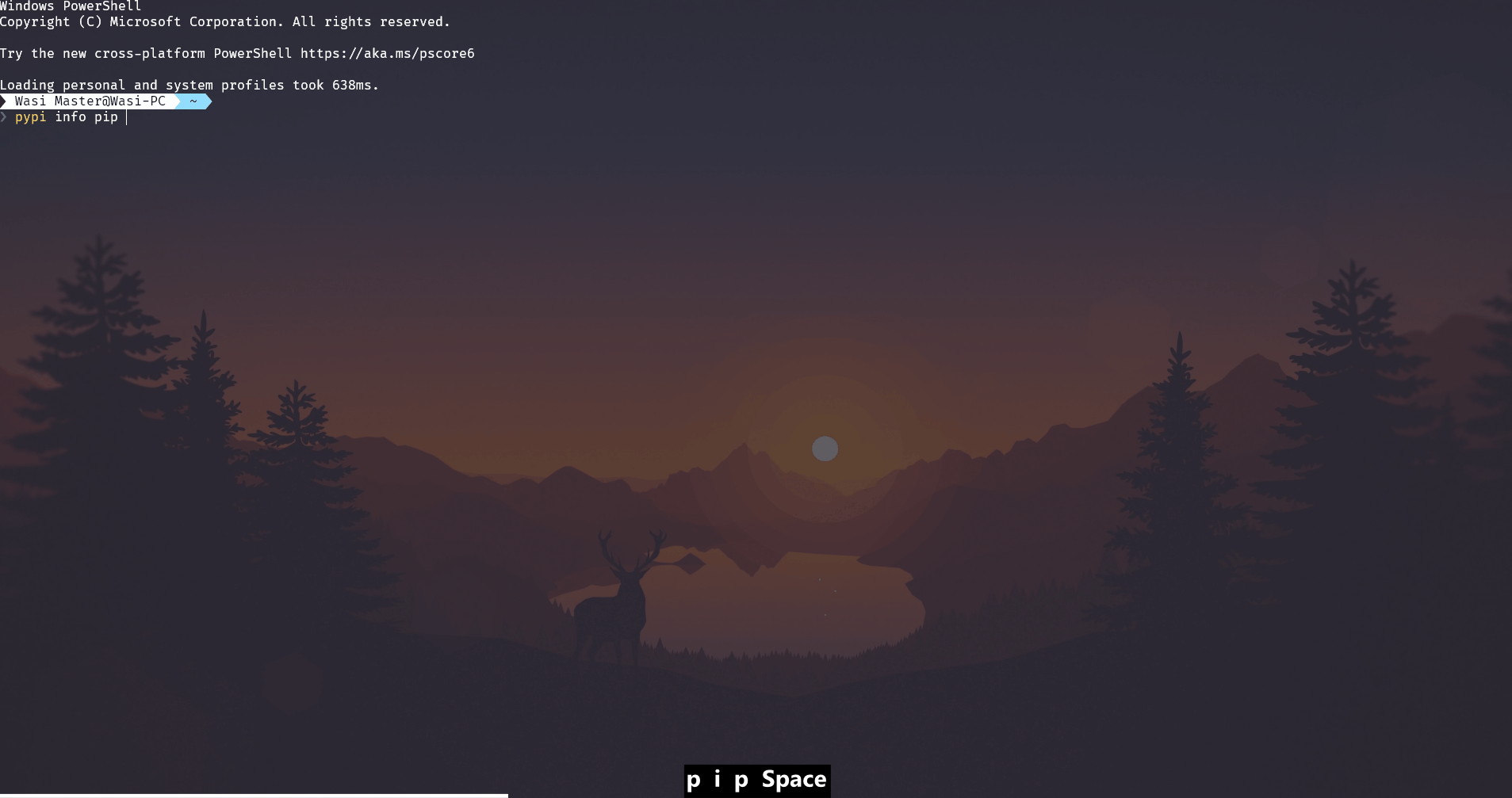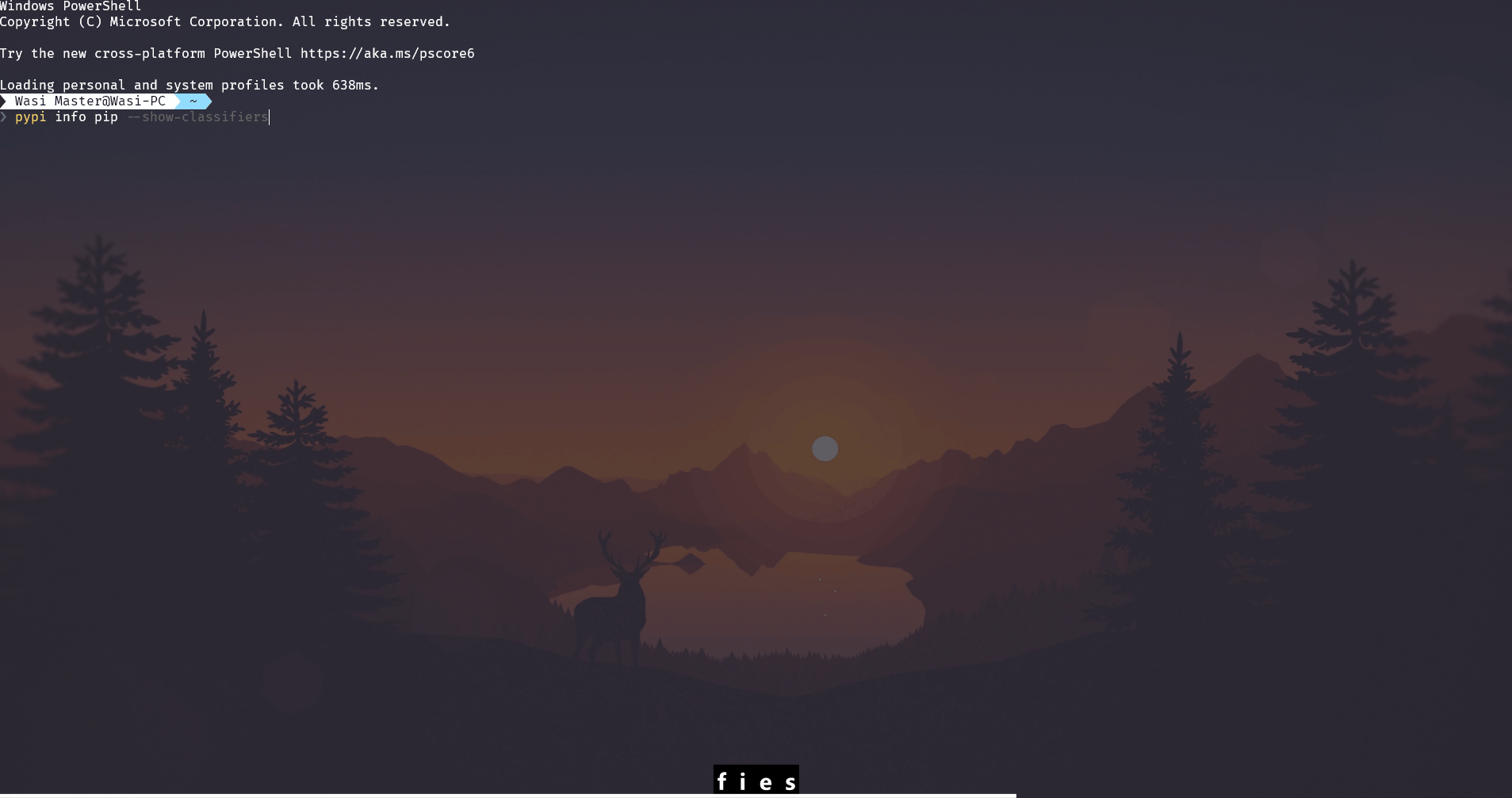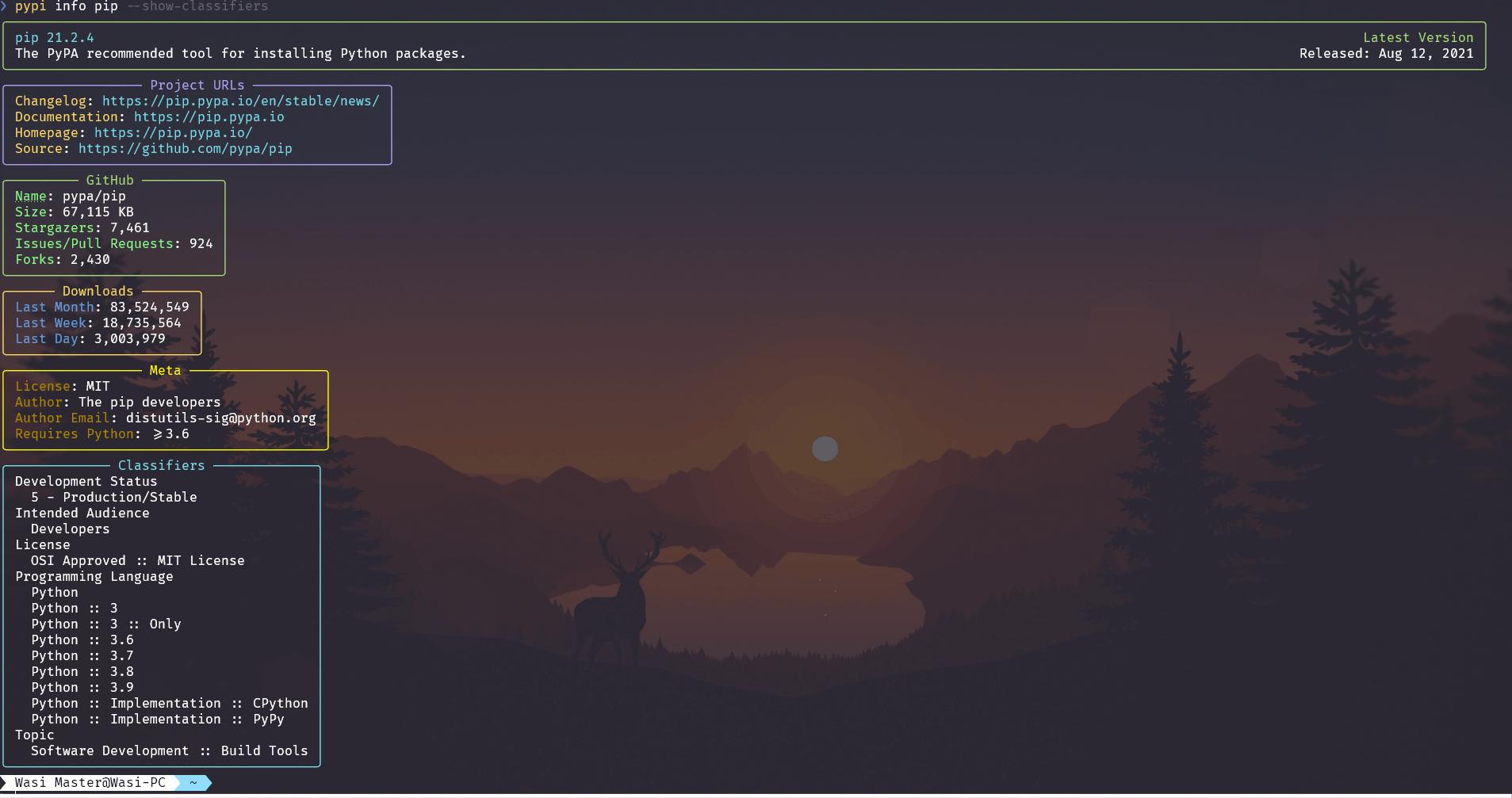
Usage¶
pypi information [OPTIONS] PACKAGE_NAME
Options¶
-
PACKAGE_NAME [required] The name of the package to show information for This can also include the version with this format:
package_name==version -
--version TEXTThe version of the package to show information for
-
--show-classifiersShow the classifiers Example of how this looks:

-
--hide-project-urlsHide the project urls
-
--hide-requirementsHide the requirements
-
--hide-githubHide the github
-
--hide-statsHide the stats
-
--hide-metaHide the metadata
-
-h,--helpShow the help message.
Errors and Warnings¶
-
E: Project not found¶
Shown when the pypi api returns a 404 response meaning a package with the specified name most likely doesn't exist
largest-files¶
This command shows the all time largest pypi packages. The layout is simillar to the one found in PyPI
Demo¶

Usage¶
pypi information [OPTIONS]
Options¶
-
-h,--helpShow the help message.
Errors and Warnings¶
-
E: Project not found¶
Shown when the pypi api returns a 404 response meaning a package with the specified name most likely doesn't exist
new-packages¶
Shows the top 40 newly added packages. Meaning that the first ever version of those packages were uploaded from pypi a short while ago.
Usage¶
pypi new-packages [OPTIONS]
Options¶
-
-h,--helpShow the help message.
-
--show-authorIf used this also shows the author This usually shows the author's email.
-
--hide-linkIf used it does not show the project link
Errors and Warnings¶
-
W:
lxmlnot installed¶There is a known bug that occurs when lxml is not installed. It doesn't show descriptions in some cases. Please install lxml using
pip install lxml.
new-releases¶
Shows the top 100 newly updated packages. Meaning that the latest version of those packages were uploaded from pypi short while ago.
Usage¶
pypi new-releases [OPTIONS]
Options¶
-
-h,--helpShow the help message.
-
--show-authorIf used, it shows the project author too This usually shows the author's email.
-
--hide-linkIf used, it shows the project link too
Errors and Warnings¶
-
W:
lxmlnot installed¶There is a known bug that occurs when lxml is not installed. It doesn't show descriptions in some cases. Please install lxml using
pip install lxml.
releases¶
Shows all the available releases for a package.
The --link argument can be used to also show the link of the releases. This is turned off by default and the link is added as a hyperlink to the package name on supported terminals
Usage¶
pypi releases [OPTIONS] PACKAGE_NAME
Options¶
-
PACKAGE_NAMEThe name of the package to show releases for This can also include the version with this format:
package_name==version -
-h,--helpShow the help message.
-
--version TEXTThe version of the package to show information for
-
--show-linksIf enabled it shows the wheel links too
Errors and Warnings¶
-
E: Project not found¶
Shown when the pypi api returns a 404 response meaning a package with the specified name most likely doesn't exist
regex-search¶
Regex stands for Regular Expressions. It allows you to search for all packages in PyPI and only show ones that match a specific Regular Expression
If the packages cache is empty it then loads the packages first, the cache is kept for 1 day meaning your data is at most 1 day old. if you want to refresh you may do so by using the cache-refresh command. For more information about this cache see notes.
Demo¶

Usage¶
pypi regex-search [OPTIONS] REGEX
Options¶
-
REGEXThe regular expression to search with [required] -
--compactCompact formatting This removes the table and just shows the package names seperated by commas, it also adds hyperlinks on supported terminals -
-h,--helpShow the help message.
read-the-docs¶
Searches the documentation for a certain package.
This just gets the documentation url and opens it's search results page with the given query
Usage¶
pypi read-the-docs [OPTIONS] PACKAGE_NAME [QUERY]
Options¶
-
PACKAGE_NAMEThe name or link to the docs of the package to show the documentation for [required]
-
QUERYThe query you want to read the docs for, if not passed it opens the main docs page
-
--url-onlyOnly print the url to the console instead of opening it in a browser[default: url-only]
-
-h,--helpShow the help message.
Errors and Warnings¶
-
W: Docs not available¶
Shown when the docs are not in the list of already known docs and needs to be gotten from PyPI, it will ask you if you want to get it from pypi
-
E: Documentation url not found on PyPI¶
Shown when the docs are not in the list of already known docs and not given on PyPI
Errors and Warnings¶
-
E: Project not found¶
Shown when the pypi api returns a 404 response meaning a package with the specified name most likely doesn't exist
search¶
Search for a package on PyPI.
Demo¶
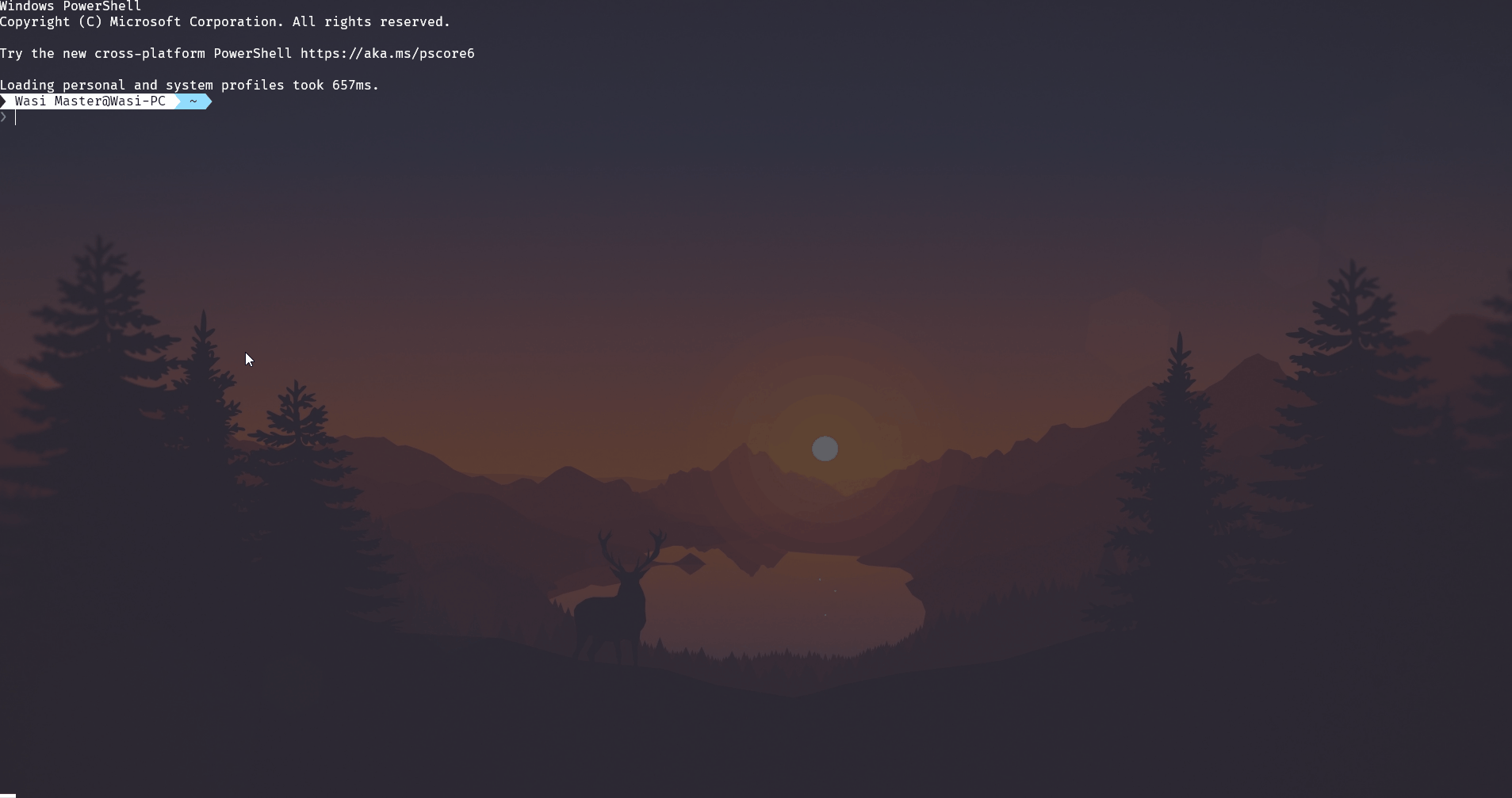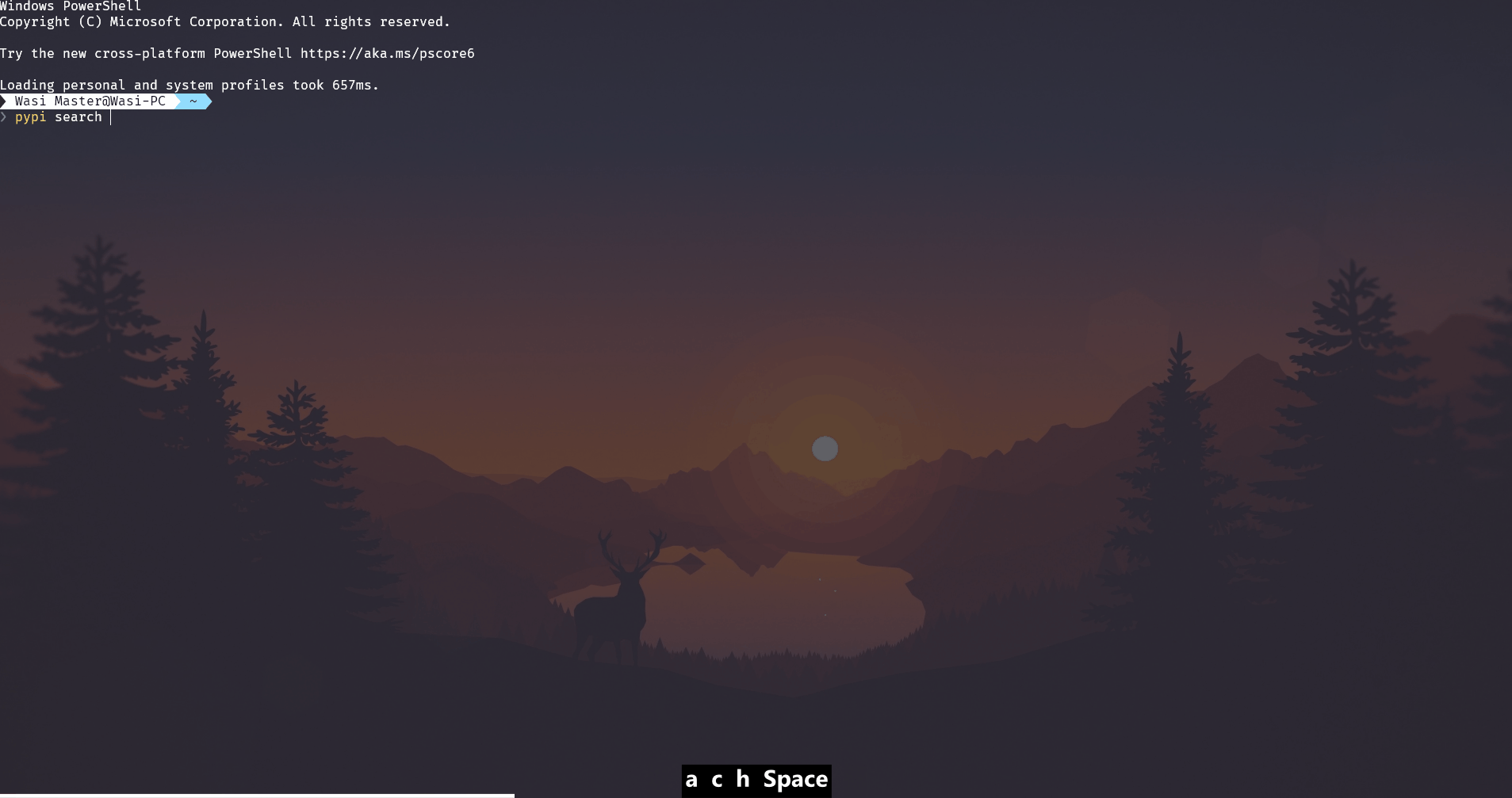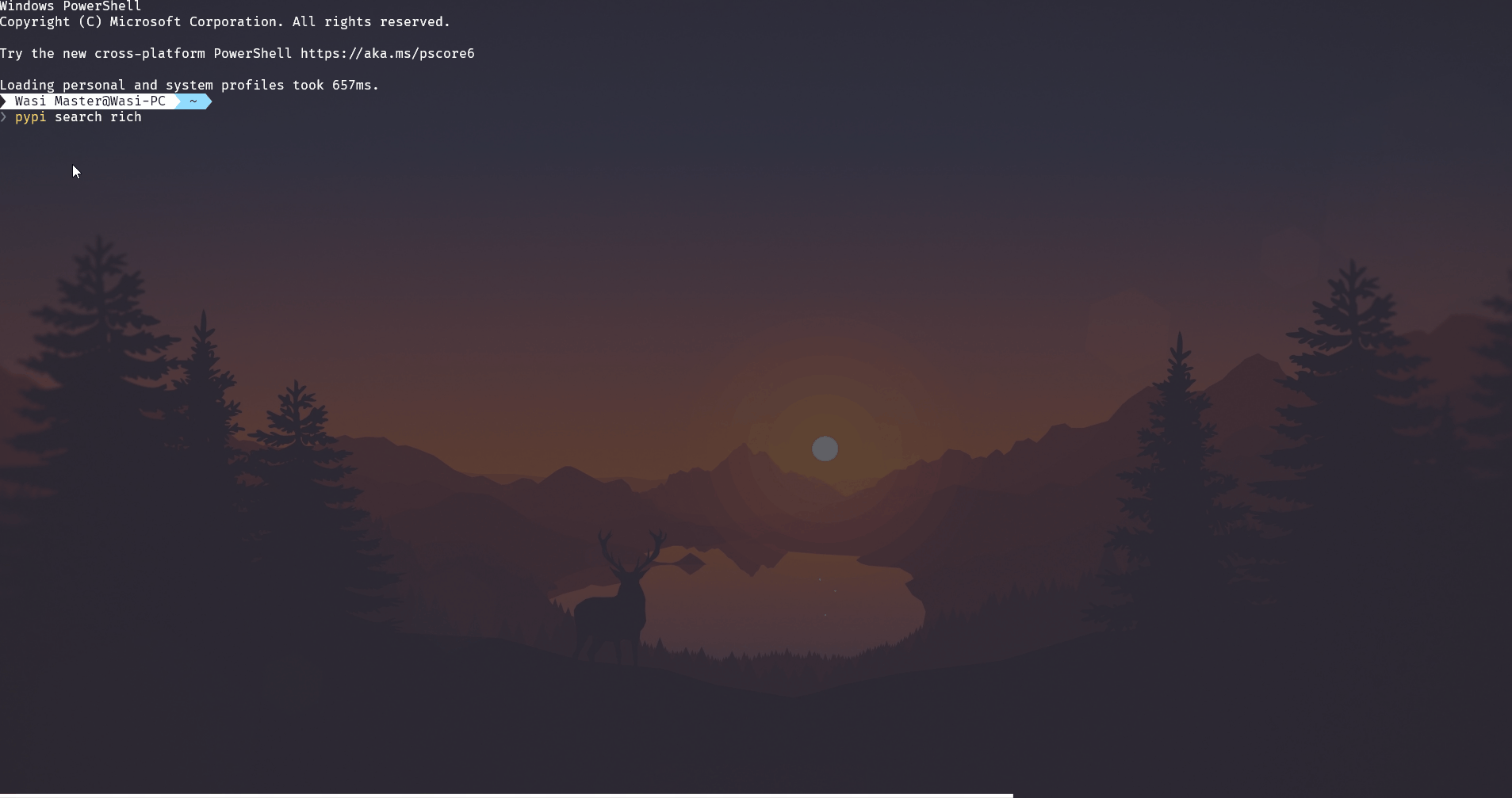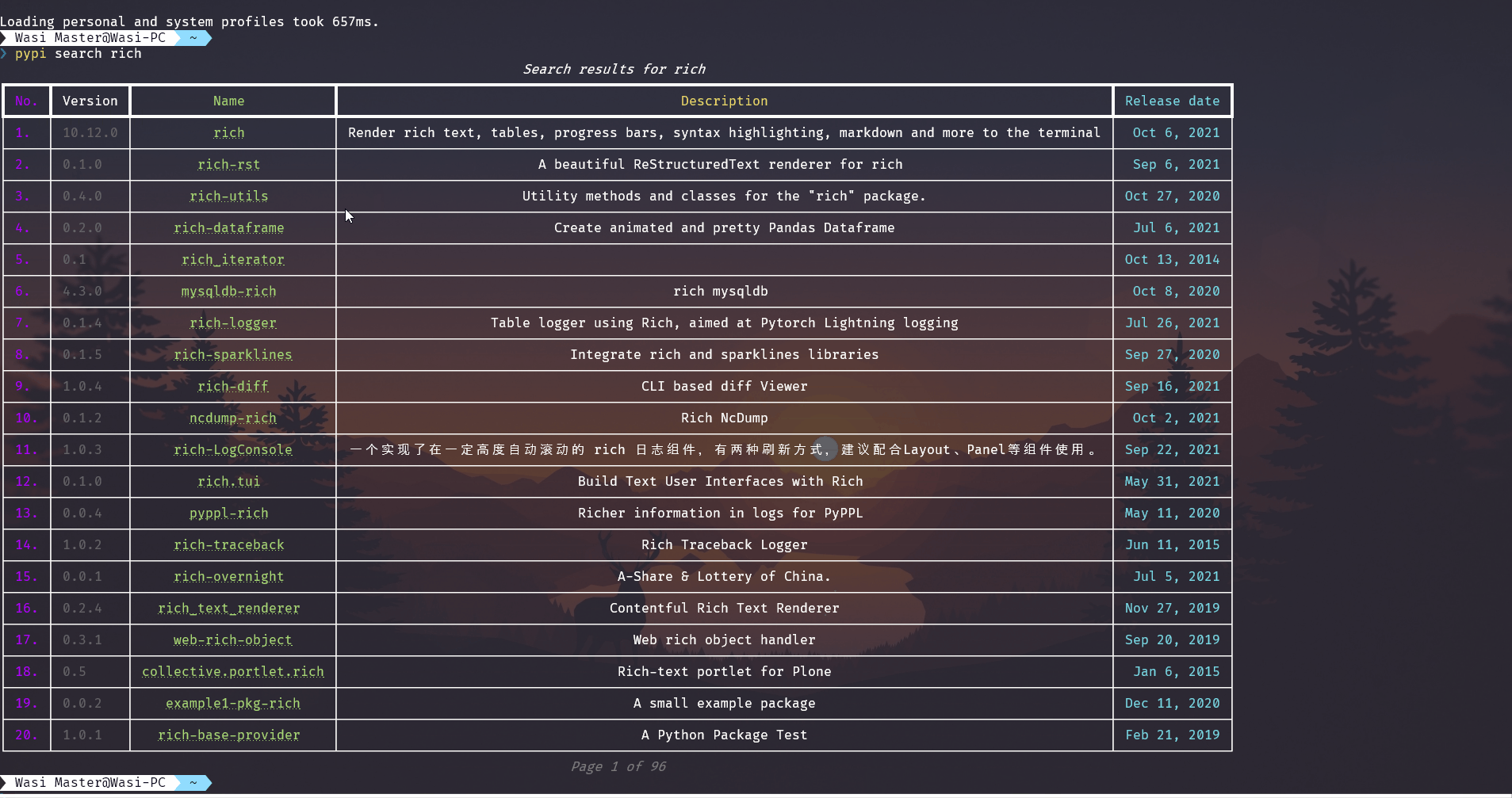
Usage¶
pypi search [OPTIONS] PACKAGE_NAME
Options¶
-
PACKAGE_NAMEThe name of the package to show wheels for [required]
-
--page INTEGER RANGEThe page of the search results to show. [default: 1; should be greater than 1 and less than 500] For example:
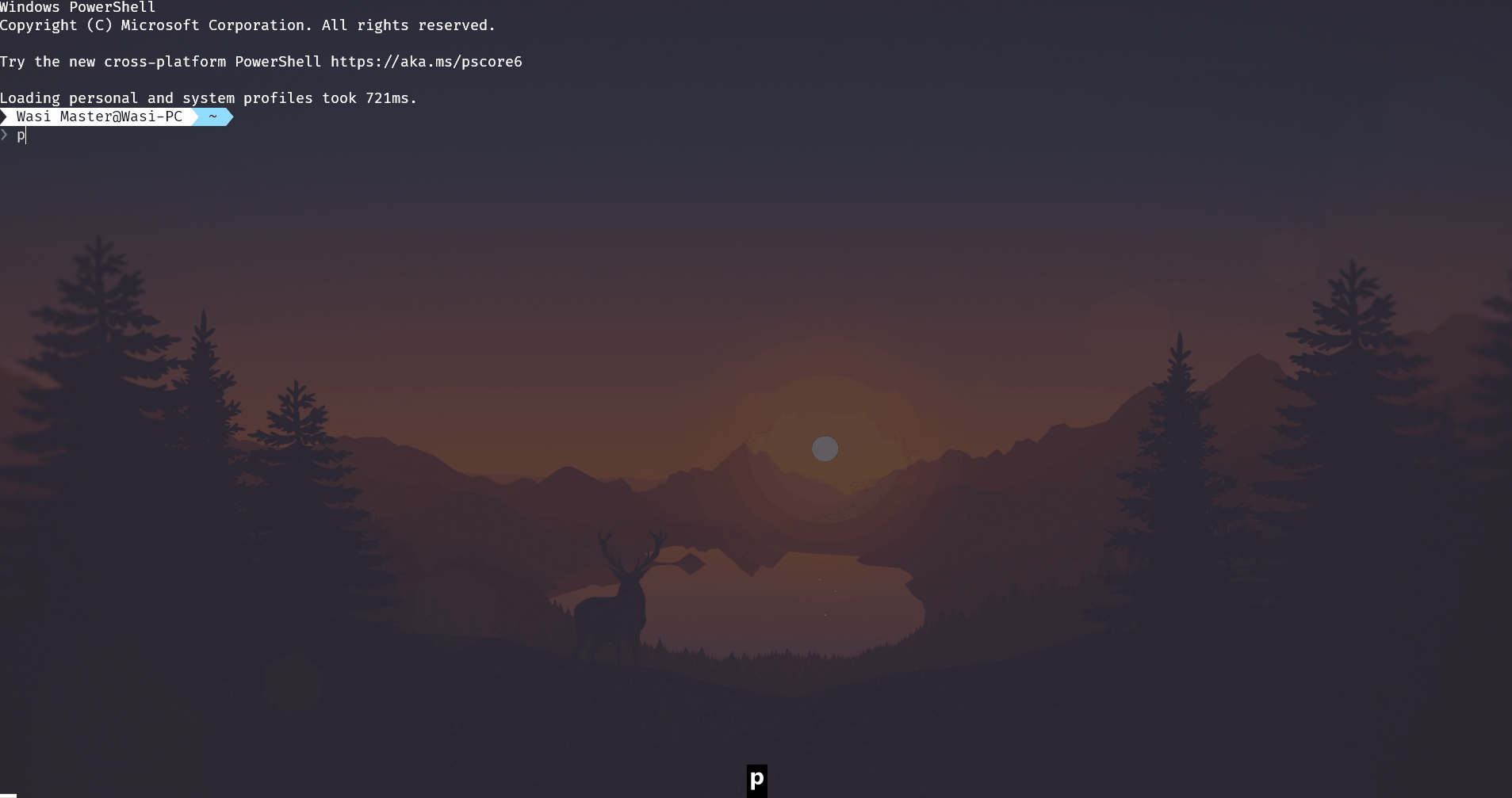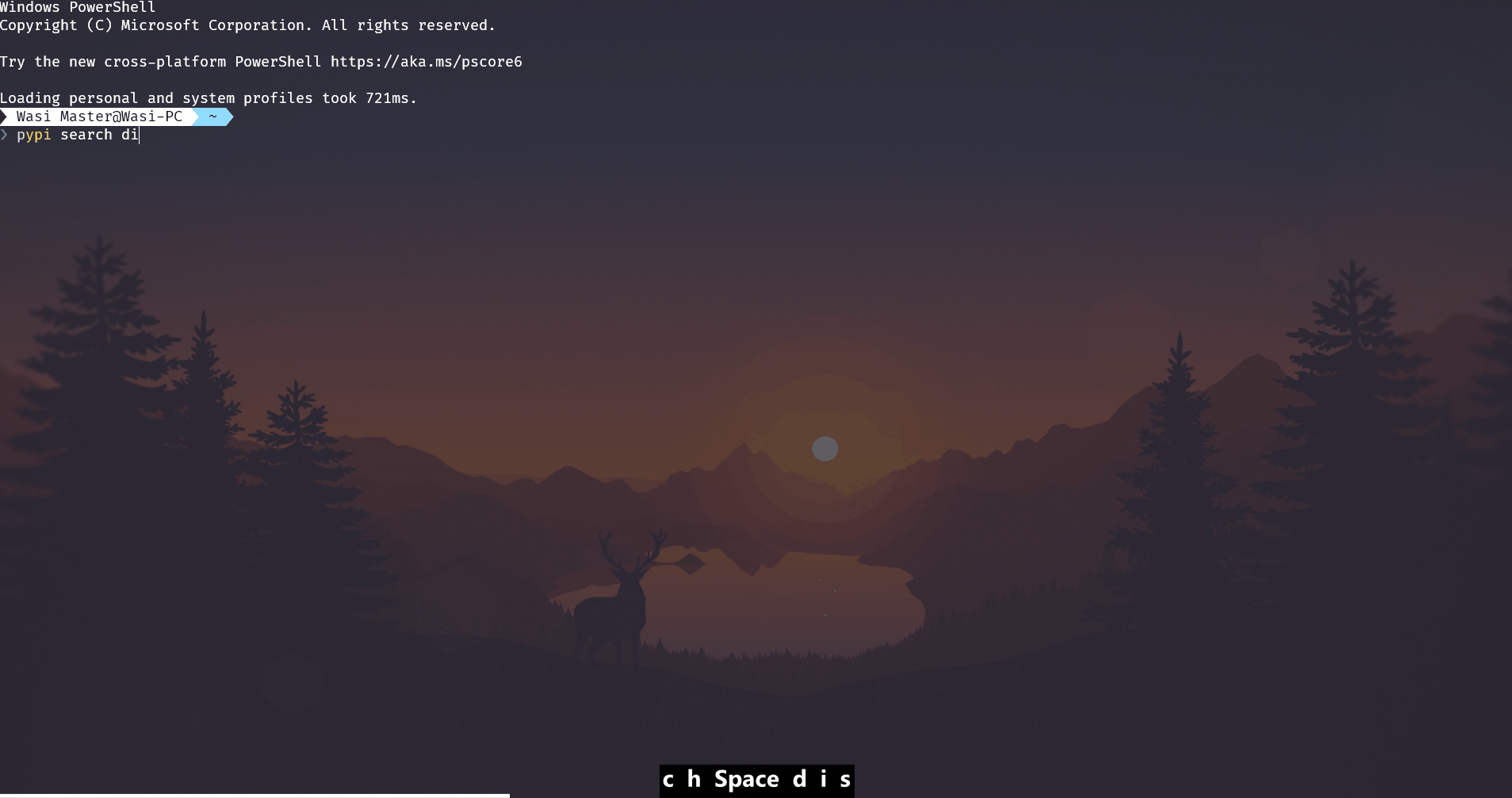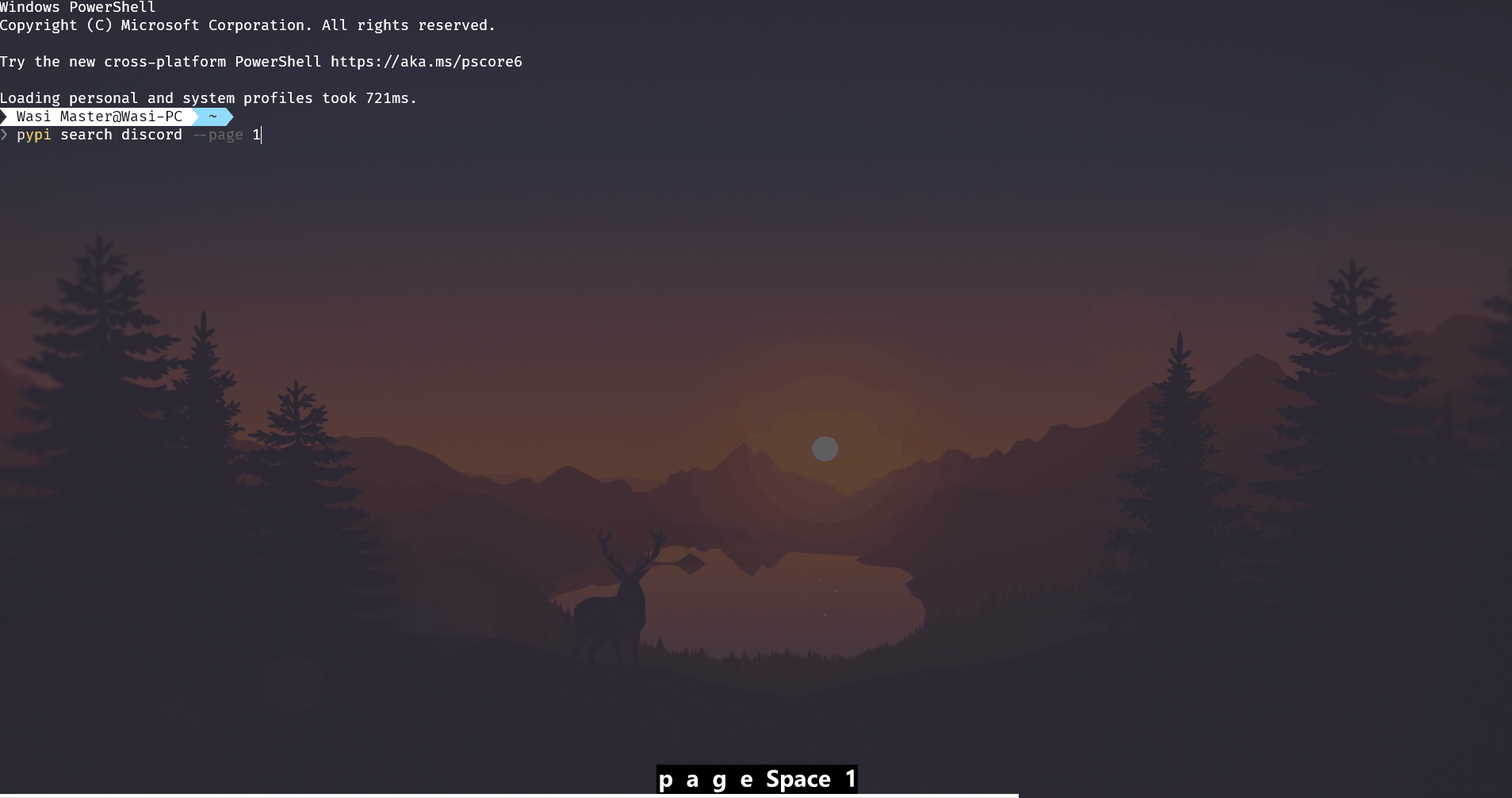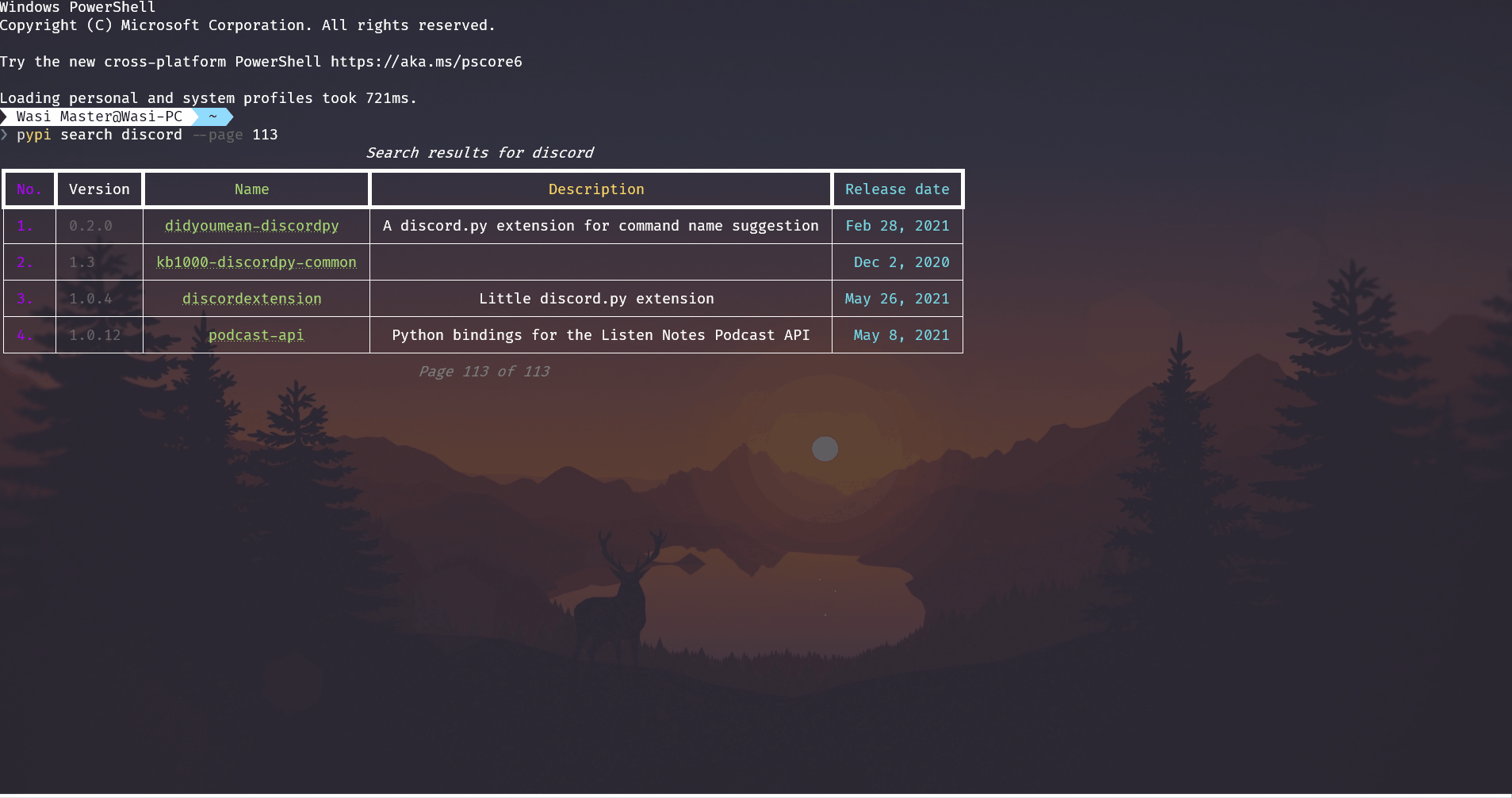
-
-h, --help
Shows the help message.
Errors and Warnings¶
E: Project not found¶
Shown when the pypi api returns a 404 response meaning the page number specified most likely doesn't exist
wheels¶
See the available wheels of a release on PyPI. The wheel names are color coded and the information is colored too.
Demo¶

Usage¶
pypi search [OPTIONS] PACKAGE_NAME [VERSION]
Options¶
-
PACKAGE_NAMEThe name of the package to show wheel info for [required]
-
VERSIONThe version of the package to show info for, defaults to latest
-
-h,--help`Shows the help message.
-
--supported-only
Only show wheels supported on the current platform
Wheel Name Syntax¶
The wheel filename is {distribution}-{version}(-{build tag})?-{python tag}-{abi tag}-{platform tag}.whl.

distribution
- Distribution name, e.g. 'pypi_command_line', 'django'.
version
- Distribution version, e.g. 1.0.
build tag (Optional)
- build number. Must start with a digit. Acts as a tie-breaker if two wheel file names are the same in all other respects (i.e. name, version, and other tags). Sort as an empty tuple if unspecified, else sort as a two-item tuple with the first item being the initial digits as an
int, and the second item being the remainder of the tag as astr.
language implementation and version tag
- E.g. 'py27', 'py2', 'py3'.
abi tag
- E.g. 'p33m', 'abi3', 'none'.
platform tag
- E.g. 'linux_x86_64', 'any'.
file extension
- E.g. '.whl'.
For example, distribution-1.0.0-1-py27-none-any.whl is the first build of a package called 'distribution' with version 1.0.0, and is compatible with Python 2.7 (any Python 2.7 implementation), with no ABI (pure Python), on any CPU architecture.
The last three components of the filename before the extension are called "compatibility tags." The compatibility tags express the package's basic interpreter requirements and are detailed in PEP 425.
- Data gotten from https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0427/#file-name-convention